Evaluation of the effect of shodhana (detoxification) process using chromatographic profiling (HPTLC,HPLC,LC-MS,and GC-MS) and estimation of the content of toxic colchicine in Gloriosa superba Linn.tubers
Ajy Kumr Meen ,Poorn Venktrmn ,Mohit Motiwle ,Rvindr Singh ,Kusum Gnji ,N.Sriknth ,K.S.Dhimn
a Regional Ayurveda Research Institute,Aamkho,Gwalior 474009,India;
b Captain Srinivasa Murthy Central Ayurveda Research Institute,Chennai 600106,India;
c Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences,Ministry of AYUSH,Govt.of India,New Delhi 110058,India
Abstract Shodhana (purification/detoxification) is an important aspect of Ayurveda.It has been described in several important pieces of literature.In this study,we performed shodhana process on Langali (Gloriosa superba Linn.) tubers of family Liliaceae,a semi-woody herbaceous climber with significant therapeutic properties.We compared the unprocessed (before purification)and processed (after purification) samples based on the phytochemical,physicochemical,and chromatographic study,including HPTLC,HPLC,GC-MS and LC-MS.Significant changes were observed in profiling after the shodhana process.This plant contains colchicine,known for its toxic effects,particularly cardiotoxicity.Therefore,we quantified colchicine in the unprocessed and processed samples of Gloriosa superba Linn.tubers using HPLC method.Results showed that the percentage of colchicine was reduced by 13.67% in chloroform extract and 20.97% in ethanol extracts after the shodhana process.
Keywords: Shodhana;HPLC;LC-MS;GC-MS;colchicine;Gloriosa superb; toxicity;Ayurveda
1 Introduction
Ayurveda is a medical system based mainly on the plants and plant products besides mineral,metallic,and animal products.Among the drugs of herbal origin,certain plants known for their toxic effects are categorized under visha (poisonous)and upavisha (semi-poisonous) drugs and are used either as a single drug or as an ingredient of compound formulas.A list of poisonous plants has been provided in Schedule E-1 of Drugs &Cosmetics Rule,1945 [1-3].Since safety is the top priority in the development and quality control of herbal medicines and products for healthcare,Ayurveda emphasizes that these poisonous drugs can only be administered only after being treated with Shodhana (detoxification),a process of purification/detoxification of herbal or mineral raw materials and also a method to enhance the potency and efficacy of the drugs [4,5].
In India and China,a number of medicinal herbs are indicated for specified therapy before they are applied for pharmacological purposes.The processing of aconite in India started in the 5th and 6th centuries and became popular in the 8th and 9th centuries.Rasashastra,the classical science of pharmacy,has been routinely used by Indian herbal medicine practitioners since the 8th century.Processing methods in Ayurveda (called Samskaras) consist of two stages: The Shodhana and Bhaishajya kalpana (formulation methods).The process of Shodhana involves the treatment of the drug with Gomutra (cow urine) and Godugdha (cow milk).The Shodhana process has been described in various languages in approximately 200 medical texts,among which “Charaka Samhita” is known for establishing the fundamental concepts for processing herbal medicines [4,6].
Langali(Gloriosa superbaLinn.),a semiwoody herbaceous climber of the Liliaceae family,has been used in inflammation,gout,rheumatoid arthritis,gonorrhea,fever and in promoting labor pains [7].In Ayurveda,Gloriosa superbais indicated for the management of Aparapatana (removal of the placenta),Mudhagarbha (dead foetus),Vrana(wound),Agnimandya (loss of appetite),Jvara (fever),Grahani (irritable bowel syndrome),Kasa (cough),Hikka (hiccough),Kushtha (leprosy),Shvitra(leucoderma),etc.[4,8].Roots ofGloriosa superba,officially approved in ayurvedic system of medicine,contain colchicine which has been reported for its toxicity,particularly cardiotoxicity [9-13].
Gloriosa superbatubers contain benzoic acid,salicylic acid,sterols and resinous substances like colchicines,3-demethyl colchicine,1,2-didemethyl colchicine,2,3-didemethyl colchicine,N-formyl,N-deacetyl colchicines,colchicocide,gloriosine,tannins and superbine [14].Colchicine (Fig.1a)is the major compound isolated from the seed and rhizome of this plant,and another important compound is gloriosine [15-17].Gloriosa superbatubers contain 0.25% colchicine apart from sitosterol,glucoside,βandγlumicolichicines,β-sitosterol,flucoside and 2-H-6-MeO benzoic acid[18,19].
In the present study,we attempted to investigate the effect of shodhana onGloriosa superbatubers(Fig.1b) by physicochemical,phytochemical study and HPLC,HPTLC,GC-MS,and LC-MS chemical profiling.Besides,the content of colchicine inGloriosa superbatubers before and after shodhana

Fig.1 (a): Chemical structure of colchicine;(b): Raw tubers of Gloriosa superba
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Collection of plant material
The Langali(Gloriosa superbaLinn.) tubers were procured from the local crude drug market Chennai,Tamilnadu and authenticated at Botany Department,Captain Srinivasa Murthy Regional Ayurveda Drug Development Institute,Chennai,with the help of flora.A specimen voucher was submitted to the department of Botany of the Institute.
2.2 Shodhana Procedure
Tubers ofGloriosa superbawere cleaned and separated from foreign matter.The tubers were cut into small pieces and soaked in Gomutra (cow urine)for 24 h.After that,it was washed and dried in the air.Finally,the dried material was pulverized and used for further research [20-22].
2.3 Phytochemical study
Preliminary phytochemical results showed the presence or absence of certain phytochemicals in theGloriosa superbatubers before and after the shodhana process.Various qualitative tests were carried out on the alcoholic extracts to identify the phytoconstituents present in the tuber samples [23,24].
2.4 Physicochemical parameters
Physicochemical parameters like total ash,acid-insoluble ash,water-soluble ash,pH of 10%w/vaqueous solution,and extractive values were determined according to the Ayurvedic pharmacopeia of India and WHO Quality Control Methods for Medicinal Plant Materials guidelines [24-27].
2.5 Chemical profiling of Gloriosa superba tubers
The detailed method of chromatographic profiling was given below:
2.5.1 HPTLC profiling
We extracted the dried powdered tubers ofGloriosa superbabefore and after shodhana process with 200 mL of ethanol using soxhlet extraction for 24 h.The extracts were evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure.We followed the same procedure for chloroform extraction.The weight of the residues obtained by extraction was given in Table 1.

Table 1 Extractive values of Gloriosa superba tubers before and after shodhana process
The residues obtained from ethanol and chloroform extracts were weighed and dissolved in methanol in 10 mL volumetric flasks,filtered through 0.22μmembrane filters,and used for HPTLC fingerprint profiling and identification of the reference standard colchicine.
2.7 mg of colchicine was accurately weighed and taken into a 10 mL volumetric flask,and 10 mL HPLC grade methanol was added to obtain 0.27 mg/mL colchicine stock solution.15μL of the test solution of chloroform and ethanol extracts and standard colchicine solution were applied on different tracks of 0.2 mm thick precoated silica gel 60 F254TLC plate (E.Merck).The plate was developed in a Toluene: Ethyl acetate: Chloroform: Methanol:Formic acid(5:3.5:0.5:0.5:0.5) solvent system to a distance of 8 cm.The plate was observed through TLC Visualizer under UV at 254 nm and 366 nm,and photos were documented.Finally,the plate was dipped in vanillin-sulphuric acid reagent and heated in a hot air oven at 105 °C until the color of the spots appeared.Photo was documented under white light.Before derivatization,the plate was scanned under UV 254 nm and 366 nm using the deuterium lamp and mercury lamp,respectively.After derivatization,the plate was scanned under UV 540 nm using the tungsten lamp.Rfvalues and fingerprint data were recorded using WIN CATS software [28-32].
2.5.2 HPLC chromatographic profiling of Gloriosa superba tubers
The residues obtained from chloroform and ethanol extracts before (unprocessed) and after (processed) shodhana process samples were accurately weighed in the same amount,dissolved in methanol in 5 mL volumetric flasks,filtered through 0.22μmembrane filters,and used for HPLC analysis chromatographic profiling.The processed and unprocessed samples were compared under the same chromatographic conditions [33-35].
The chromatographic conditions were given below:
? Column type:
ZORBAX Eclipse XBD-C18(4.6 mm×150 mm)
5μm particle size
? Mobile Phase:
Phosphate Buffer : Acetonitrile (70:30)
? Detection:
DAD detector @ 230 nm
? Flow Rate:
1.0mL/min
? Injection Volume: 10μL
2.5.3 GC-MS chromatographic profiling of Gloriosa superba tubers
The test solution was prepared by dissolving the dried extracts of chloroform in chloroform and methanol solvents of the required volume.The solution was filtered and sent for GC-MS analysis.The processed and unprocessed samples were compared under the same chromatographic conditions.
2.5.4 LC-MS chromatographic profiling of Gloriosa superba tubers
The test solution was prepared by dissolving ethanol extracts ofGloriosa superbatubers before(6.1 mg) and after (6.0 mg) shodhana process in HPLC grade methanol (up to 1.0 mL volume).It was filtered and sent for LC-MS analysis.
The processed and unprocessed samples were compared under the same chromatographic conditions.
2.6 Quantitative estimation of colchicine in Gloriosa superba tubers by HPLC
The residues obtained from chloroform and ethanol extracts ofGloriosa Superbatubers before and after shodhana process were accurately weighed in triplicate and dissolved in methanol in 5 mL volumetric flasks,filtered through 0.22μmembrane filters,and used for HPLC analysis.
2.7 mg of colchicine reference standard was accurately weighed,transferred to a 10 mL volumetric flask,and dissolved in HPLC grade methanol.The solution was made up to 10 mL to obtain 0.27 mg/mL colchicine stock solution.
The chromatographic conditions were given below:
Column-ZORBAX Eclipse XBD-C18(4.6 mm×150 mm),5μm particle size
Detection-DAD Detector at 245 nm
Mobile phase-Water: Acetonitrile (70:30)
Flow rate-1.0 mL/min
Injection volume-10μL
Mode of Operation-Isocratic elution
Retention time-3.410
0.27 mg/mL colchicine stock solution was appropriately diluted to give 0.1350,0.0675,0.0337 and 0.0169 mg/mL of colchicine standards.Each standard solution was analyzed by HPLC and the respective peak areas were recorded.We established the calibration curve for peak area vs.concentration of colchicine applied.10μL of each test solution was injected into the HPLC system.The chromatogram was recorded,and the peak area of the test solution was determined corresponding to that of colchicine as described above from the calibration curve.The amount of colchicine present in the residues of the ethanol and chloroform extracts for each test sample was calculated forGloriosa superbatuber samples before and after shodhana process.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Preliminary phytochemicals screening
Preliminary phytochemical screening results showed the presence or absence of certain phytochemicals in theGloriosa superbatubers.The preliminary comparative phytochemicals screening results ofGloriosa superbatubers before and after the shodhana process were shown in Table 2.

Table 2 Preliminary phytochemicals screening of Gloriosa superba tubers before and after shodhana process
3.2 Physicochemical parameters
We carried out Physico-chemical analysis to ascertain the quality of the raw material used in the study.The comparative analysis results of physicochemical parameters forGloriosa superbatubers samples before and after shodhana processes were shown in Table 3.The results of all the parameters complied with the Ayurvedic Pharmacopeia of India (API) standards.

Table 3 Physicochemical parameters of Gloriosa superba tubers before and after shodhana process
Compared to the unprocessed sample,the percentage of water-soluble extractive,alcohol soluble extractive,ash content,and acid-insoluble ash in the processed sample decreased,and the loss on drying at 105 °C and pH increased.
3.3 Chemical profiling of Gloriosa superba tubers
Chromatographic profiling was performed using four different chromatographic techniques to study the effect of the shodhana process on theGloriosa superbatubers.The details of chromatographic profiling were given below.
3.3.1 HPTLC chromatographic profiling of Gloriosa superb tubers
Comparative HPTLC fingerprint profile was given in Fig.2.A band at 254 nm (dark green,Rf0.19) corresponding to colchicine reference standard was observed in both the standard and test solution tracks of chloroform and ethanol extracts ofGloriosa superbatubers before and after the shodhana process.

Fig.2 HPTLC fingerprint profiling of Gloriosa superba tubers chloroform and ethanol extracts of before and after shodana process and colchicine reference standard
3.3.2 HPLC chromatographic profiling of Gloriosa superba tubers
In comparing HPLC Chromatographic profiling of chloroform extracts,17 peaks in unprocessed and 8 peaks in processed samples were detected.17 peaks in unprocessed and 19 peaks in processed samples of each ethanol extract were detected.The peak area of all processed samples was reduced compared to unprocessed samples.The detailed peak identification and peak area results were shown in Figs.3-4 and Tables 4-5.
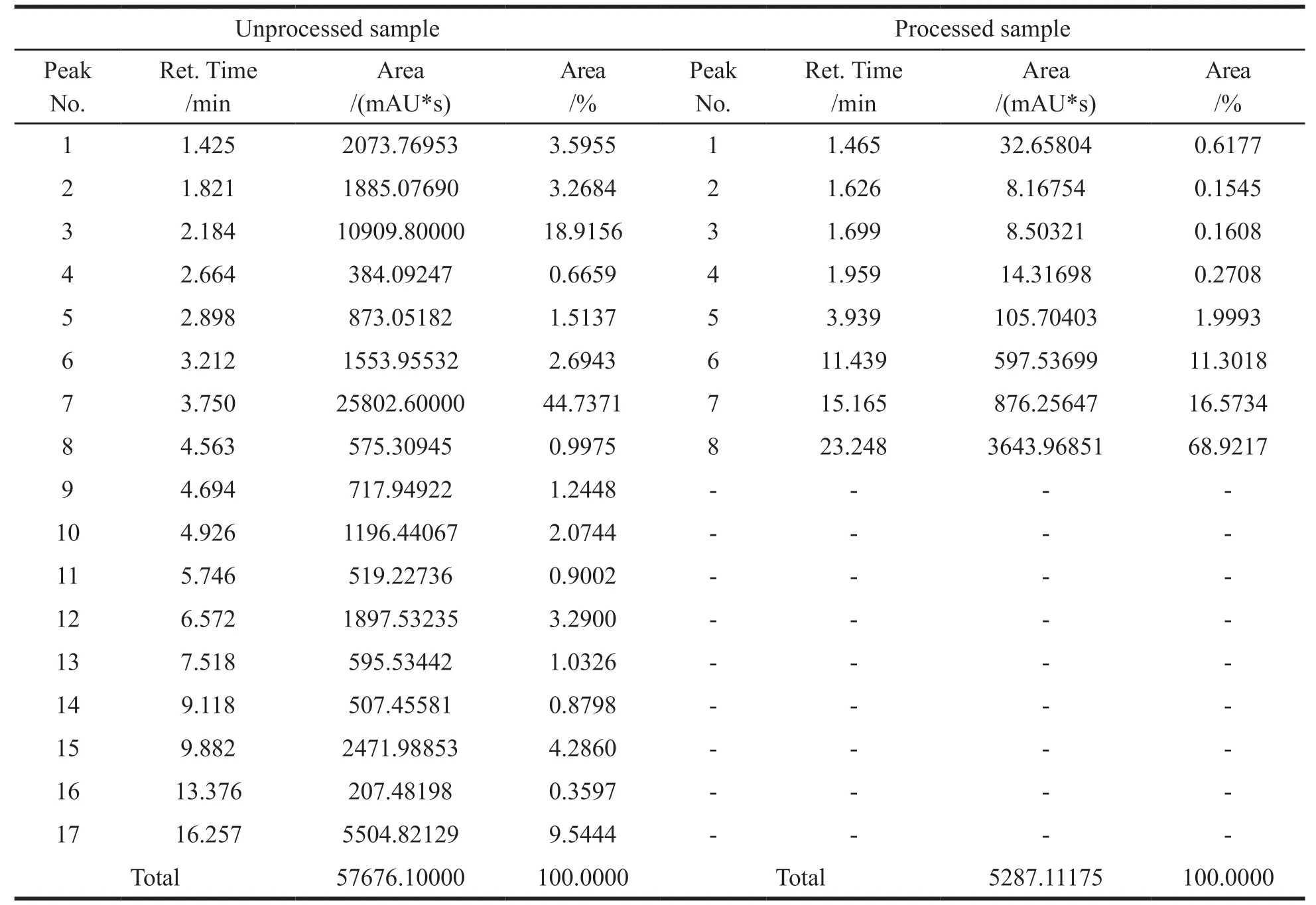
Table 4 HPLC peak details of Gloriosa superba chloroform extracts before and after shodhana process

Table 5 HPLC peak of Gloriosa superba ethanol extracts before and after shodhana process

Continued table 5

Fig.3 HPLC profiling chromatogram of Gloriosa superba tubers chloroform extracts before and after shodhana process (Rentention Time in Min.)

Continued fig.3

Fig.4 HPLC profiling chromatogram of Gloriosa superba tubers ethanol extracts before and after shodhana process(Rentention Time in Min.)
3.3.3 GC-MS chromatographic profiling of Gloriosa superba tubers
GC-MS analysis of chloroform extracts ofGloriosa superbashowed 13 peaks in unprocessed sample and 16 peaks in the processed sample.The detailed peak identification was shown in Fig.5,and retention time,peak area,area percentage,compound name,and molecular weight were given in Table 6.Remarkable changes were observed in the chloroform extracts according to GC-MS profiling chromatograms of theGloriosa superbatubers before and after the shodhana process.Mass spectrum GC-MS was interpreted using the database of the National Standard and Technology (NIST)library.We compared the spectrum of the unknown component with the spectrum of the known components stored in the NIST library.Structures of compounds were shown in Figs.6-7.

Continued table 6
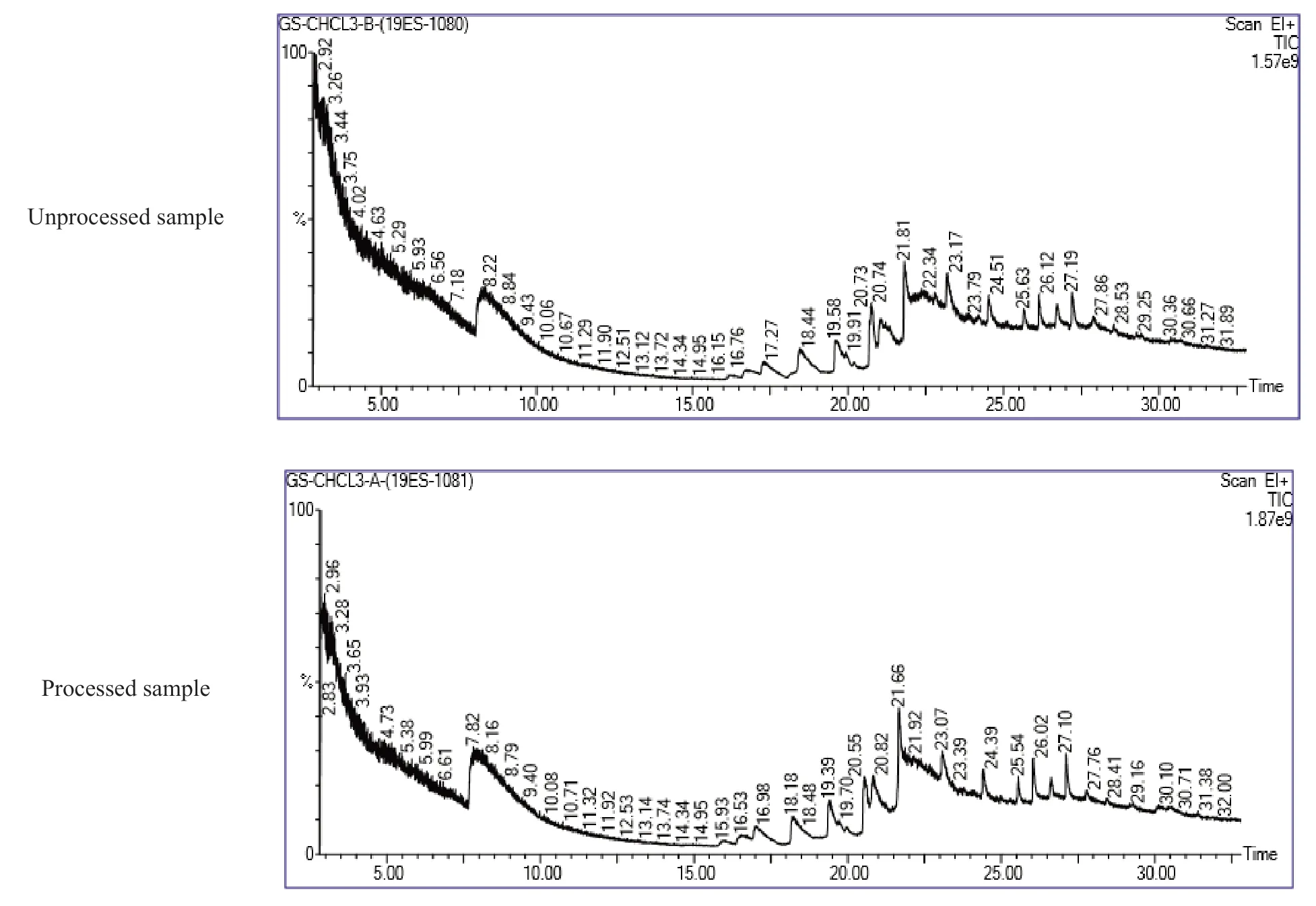
Fig.5 GC-MS chromatogram of Gloriosa superba chloroform extracts before and after shodhana process (Rentention Time in Min.)
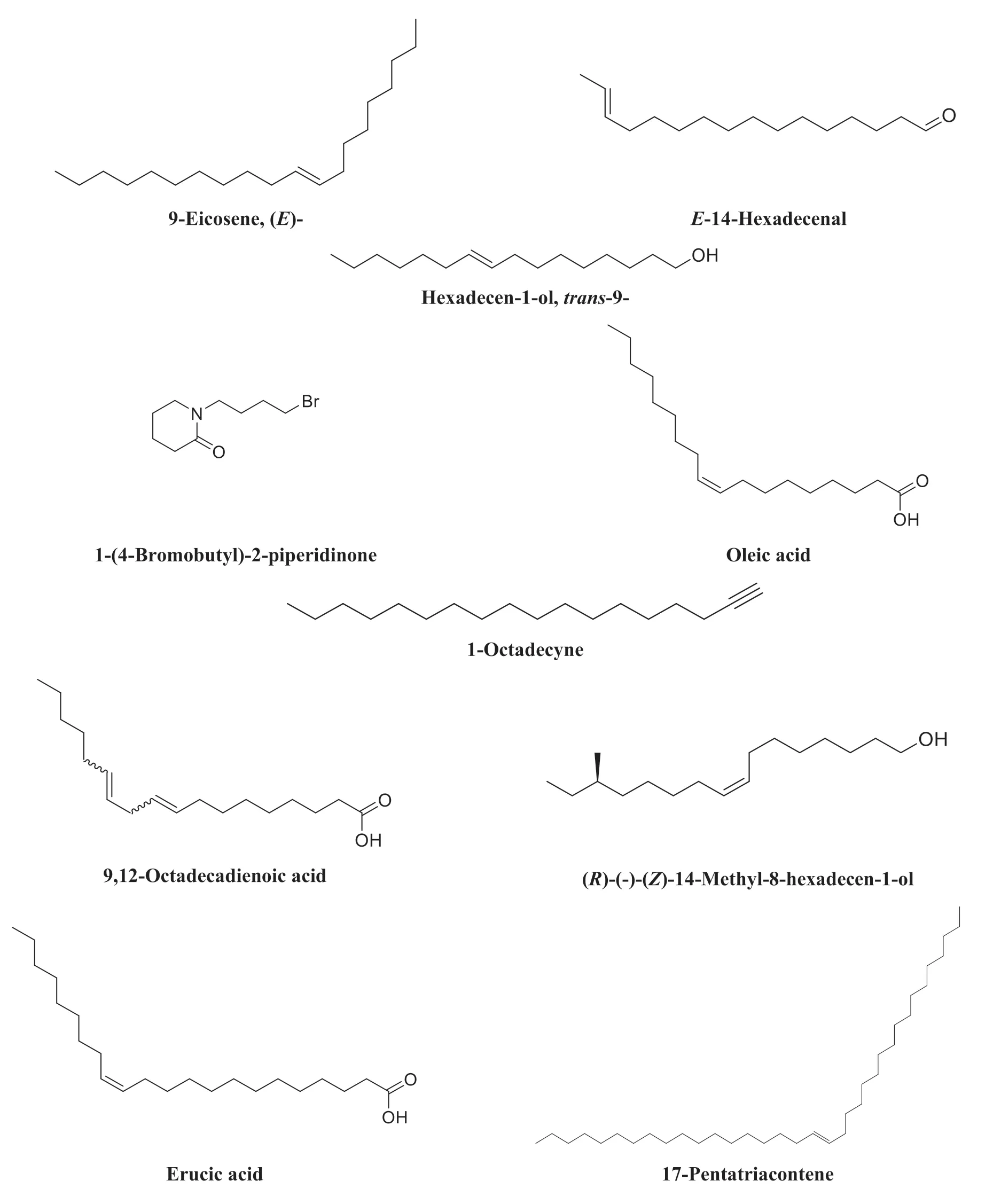
Fig.6 Compounds identified by the GC-MS analysis of Gloriosa superba chloroform extracts before shodhana process

Continued fig.6

Fig.7 Compounds identified by the GC-MS analysis of Gloriosa superba chloroform extracts after shodhana process

Continued fig.7
3.3.4 LC-MS chromatographic profiling of Gloriosa superba tubers
LC-MS Chromatographic profiling of ethanol extracts ofGloriosa superbatubers showed the presence of 23 peaks in the unprocessed sample and 29 peaks in the processed sample.The detailed peak identification was shown in Fig.8,and retention time,peak area,and area percentage were given in Table 7.Remarkable changes were observed in the LC-MS profiling chromatograms of the the ethanol extracts ofGloriosa superbatubers before and after the shodhana process.

Table 7 LC-MS peaks details of Gloriosa superba tubers ethanol extracts before and after shodhana process

Continued table 7

Fig.8 LC-MS chromatogram of Gloriosa superba tuber ethanol extracts before and after shodhana process

Continued fig.8

Fig.9 HPLC chromatogram of colchicine standard and standard calibration curve (Retention Time in Min.)

Fig.10 HPLC chromatogram of : (a) EB: Ethanol extract before shodhana;(b) EA: Ethanol extract after shodhana;(c) STD: Colchicine Standard;(d) CB: Chloroform extract before shodhana;(e) CA: Chloroform extract after shodhana (Retention Time in Min.)

Table 8 Estimation of colchicine in the chloroform and ethanol extracts of Gloriosa superba tubers before and after shodhana process
The results obtained from HPLC analysis revealed that the level of colchicine after the shodhana process ofGloriosa Superbatubers significantly declined as compared to unprocessed samples.HPLC analysis showed a decrease of 13.67% colchicine in chloroform extract and 20.97%in ethanol extract after the shodhana process.
4 Conclusion
In the present study,we attempted to purify theGloriosa superbatubers by the classical Ayurvedic shodhana process.We determined preliminary phytochemical screening and physicochemical parameters of theGloriosa superbatuber samples before and after the shodhana process.The percentage of water-soluble extractive,alcohol soluble extractive,ash content,acid-insoluble ash was reduced,and the loss on drying at 105 °C and pH increased in the processedGloriosa superbatubers as compared to the unprocessed sample.We observed the remarkable changes in different physicochemical parameters,HPTLC,HPLC,GCMS,and LC-MS chromatographic profiling before and after shodhana process ofGloriosa superbatubers.In the HPLC chromatographic profiling,it was observed that the peak area of all processed samples was reduced as compared to unprocessed samples.
HPLC studies revealed that the process of shodhana resulted in the depletion of colchicine,the chief toxic constituent ofGloriosa superbatubers.This study found that the percentage of colchicine was reduced by 13.67% in chloroform extract and 20.97% in ethanol extracts after the shodhana process.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgement
The authors are very grateful to the Director-General of CCRAS,Ministry of AYUSH,New Delhi,for the encouragement and facilities provided for this work.

