Carbon emission reduction effect and mechanism test of carbon emission trading pilot
YANG Xiao-xuan,ZHANG Yan-wei
School of Business,University of Jinan,Jinan 250002,CHINA
Abstract: Carbon emission trading pilot policies were launched in seven provinces and cities,including Beijing,Shanghai,Tianjin and Chongqing in 2013.Carbon emission trading is of great significance to the development of green economy.Taking China’s carbon emission trading pilot as a natural experiment,the dual difference method was used to explore the carbon emission reduction effect of the pilot carbon emission trading policy on the pilot areas in China based on the panel data of 30 provinces,autonomous regions and municipalities in China from 2000 to 2019.Propensity score matching,parallel trend test and placebo test were conducted to improve the robustness of the empirical results.It is found that carbon emission trading pilot policies significantly promote carbon emission reduction in pilot areas compared with non-pilot areas.This conclusion from the benchmark regression passed the robustness test,and the carbon reduction effect showed an increasing trend year by year.With the mediation effect test,the carbon emission reduction mechanism of the pilot policy was studied.The results show that the carbon trading pilot policy reduces the carbon dioxide emission in the pilot area by promoting the upgrading of industrial structure and technological progress.
Key words: carbon emission trading;carbon emission;DID model
1 Introduction
At present,China is vigorously developing a green economy,taking energy conservation,emission reduction and the implementation of a low-carbon economy as the important tasks of the national development,aiming to foster a new economic growth point characterized by low energy consumption,low pollution and low carbon emissions.In October 2011,the National Development and Reform Commission issued the Notice on Pilot Work of Carbon Emission Trading,which approved the pilot work of carbon trading in seven provinces and cities including Beijing,Shanghai,Tianjin,Chongqing,Hubei,Guangdong and Shenzhen.
In 2013,the“two provinces and five cities”carbon emissions trading pilot was fully launched.On July 16,2021,the national carbon emissions trading opened.In May 2022,the turnover of carbon emission quota(CEA)in the national carbon emission trading market was 2,255,100 t,with a total turnover of 128 million yuan,(with)an average turnover price of 56.81 yuan/t;As of May 31,2022,the cumulative turnover of the National Carbon Market Emission Quota (CEA) was 193million t,with a turnover of 8,419 million yuan and an average transaction price of 43.68 yuan/t(2020).
The concept of carbon emissions trading originated from economists in the 1990s,carbon market could achieve social emission reduction targets at low cost.If the enterprise’s emission reduction cost is lower than the market price of carbon,it will choose to reduce the emission,and the share of emission reduction can be sold for profit.When it is higher than the market price of carbon,it will choose to buy a quota to fulfill the emission reduction issued by the government.
Has China’s carbon emissions trading pilot policy effectively brought into play the expected effect of driving carbon emission reduction,and what is the mechanism? In order to answer the above questions,this paper uses the double difference method to explore the carbon emission reduction effect of the carbon emissions trading pilot policy on China’s pilot areas,and conducted propensity score matching,parallel trend test and placebo test to improve the robustness of the empirical results based on the panel data of 30 provinces,autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government in China from 2000 to 2019.The carbon emission reduction mechanism of the pilot policy was analyzed with the intermediary effect test.
2 Literature review
As a market-based incentive policy that can internalize externalities,the carbon emissions trading pilot policy has attracted extensive attention from scholars in recent years.Many scholars had made multi-dimensional research on this issue.The existing literature mainly studied the energy-saving and emission-reduction effects,economic effects and technological innovation effects of the policy.
Regarding the energy-saving and emission-reduction effects of carbon emission trading,Liu and Guo (2022) believed that the carbon emission trading policy could effectively promote the improvement of the energy and environmental efficiency of the pilot cities and promote the energy-saving and emission-reduction of the pilot cities,and the promotion effect of the carbon emission trading policy on the energy-saving and emission-reduction of the cities was influenced by the industrial structure of the cities,the intensity of green innovation and the development of the factor market.Li and Wang(2021)used the synthetic control method to conduct quasi-natural experiments and combined with the dynamic spatial Tobin model to comprehensively evaluate the spatial emission reduction effect of the implementation of the carbon trading policy.It was found that the carbon trading pilot policy effectively promoted the carbon emission reduction in the pilot areas as a whole,and the carbon trading pilot policy,on the basis of effectively suppressing the carbon emission in the pilot areas,helped to suppress the carbon emission in the neighboring areas through the policy spillover effect.Ji and Yang(2021)believed that the implementation of the carbon trading policy has significant carbon emission inhibition effect,which can“accelerate” the reduction of carbon emissions and carbon intensity,and the effect of emission reduction increased year by year without time lag.Jing and Chen (2022) believed that the pilot policy of carbon emission trading has significantly suppressed the emission of industrial SO2and industrial wastewater in the region.Li et al.(2022) believed that the emission reduction effect of the pilot policy of carbon emissions trading has the typical characteristics of immediacy and gradual strengthening.In the long run,the emission reduction effect is always significant and keeps improving.Liu et al.(2019)believed that the implementation of carbon emission trading pilot has reduced carbon dioxide emissions,but due to the differences in economic development and industrial structure of each pilot,the carbon emission reduction effect of each pilot province is heterogeneous.Cao and Zhong (2023) pointed out that the carbon intensity of seven pilot provinces and cities declined after the carbon trading pilot.Pan and Wang(2022)believed that the pilot work of carbon emissions trading has significantly reduced the carbon emissions of enterprises.
Regarding the research on the economic effects of carbon emissions trading,Jing (2022)pointed out that the pilot carbon emissions trading policy could significantly promote the high-quality development of the regional economy,and the pilot carbon emissions trading policy in the eastern region could promote the high-quality development of the regional economy,but the impact of the pilot carbon emissions trading policy on the high-quality development of the economy in the central and western regions was not significant.Shao and Li(2022) believed that the implementation of the carbon emissions trading pilot policy had significantly promoted the high-quality economic development,and the policy mainly improved the quality of economic development by promoting technological innovation,promoting the upgrading of industrial structure,and generating the synergistic effect of relevant environmental policies.Guo and Xiao(2022) believed that the pilot of carbon emission trading can significantly improve the level of China’s foreign direct investment.Yin et al.(2022) believed that carbon trading pilot policy effectively promoted the carbon decoupling effect in the pilot areas.Liu et al.(2023)believed that the pilot implementation of carbon emission trading can significantly boost the high-quality growth of regional economy.
In terms of research on the technological innovation effect of carbon emissions trading,Hoffmann (2007) pointed out that carbon emissions trading would increase the carbon emission reduction costs borne by enterprises in the short term,thus forcing them to actively carry out green technological innovation activities.Guo et al.(2021) indicated that China’s low-carbon technology innovation showed obvious spatial agglomeration effect in the central and eastern regions,and the establishment of carbon emission trading pilot had significantly promoted the regional low-carbon technology innovation level.Wang et al.(2020) found that the pilot policy of carbon emissions trading induced low-carbon technological innovation activities in the pilot areas as a whole by using the synthesis control method.Hu et al.(2020) believed that the implementation of the carbon emissions trading mechanism had significantly promoted the technological innovation of enterprises,and when the carbon market was more liquid,the market-based incentive environmental regulation had a more obvious role in promoting the technological innovation of enterprises.Yu et al.(2023) found that the pilot policy of carbon emissions trading significantly promoted the innovation level of the regulatory industry in the pilot area,and the conclusion was still valid after various robustness tests.Li (2022) believed that the carbon emission trading policy has significantly improved the innovation level of emission control enterprises,and the effect of this policy tends to increase with the passage of time.Liu and Wen(2023)believed that the implementation of carbon emission trading policy can effectively promote the end-governance,clean production and energy-saving green technology innovation of manufacturing enterprises.
The existing research has extensively discussed whether the carbon emission trading pilot policy can effectively drive energy conservation and emission reduction,but the research on its mechanism is not sufficient.The inadequacy of the above research makes it difficult for the existing literature to provide more accurate empirical support for the effective implementation and optimization of the important policy of carbon emissions trading.In view of this,based on the panel data of 30 provinces,autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government in China from 2000 to 2019,this paper uses the double difference method and the intermediate effect test method to conduct an empirical study on the carbon emission reduction effect and its mechanism of the pilot carbon emission trading policy so as to provide scientific decision-making basis for the development of green economy in China.
3 Model setting and variable selection
3.1 Model setting
In 2013,seven provinces and cities including Beijing,Shanghai,Tianjin,Chongqing,Hubei,Guangdong and Shenzhen successively launched pilot carbon emissions trading.This pilot policy can be regarded as a “quasi-natural experiment“.This paper used the double difference method(DID) to evaluate the emission reduction effect of the carbon emissions trading policy,taking the provinces(Beijing,Shanghai,Tianjin,Chongqing,Hubei and Guangdong)that had implemented the carbon trading pilot in 30 provinces (excluding Xizang,Hong Kong,Macao and Taiwan) as the experimental group,the non-pilot provinces as the control group,and 2013 as the starting point of the policy implementation.The dual difference method model which controls the bidirectional fixed effect was adopted to eliminate the differences between different regions and different time points,and the following dual difference measurement model was constructed:
3.2 Selection of variables
In the model,treatiis a policy virtual variable,with 1 in the pilot province and 0 in the non-pilot province.timetis a virtual variable of time,withtimetvalue of 0 before 2013 andtimettvalue of 1 after 2013.treatment,namelytreati*timet,which is the product of the aforementioned two virtual variables,is the coefficient of which measures the implementation effect of the carbon trading policy in the double difference model and is the core variable concerned by the model.is an individual fixed effect,a time fixed effect anda random error term.
The variable to be interpreted is the logarithm of carbon dioxide emissions (10000 tons),which can ensure the data to be more stable and weaken the multicollinearity and heteroscedasticity in the model to a certain extent.are control variables,includingis in order to measure the per capita GDP of each region’s economic development,expressed as the logarithm of the per capita GDP of each region;is the total population,expressed as the logarithm of the number of permanent residents in each region at the end of the year;is the industrial structure,expressed by the proportion of the secondary industry in the GDP of a province;is energy intensity,expressed as the proportion of energy consumption in the GDP of a province.
3.3 Data sources
The original data comes from the National Bureau of Statistics official website,China Economic Network Statistics Database,China Carbon Accounting Database(CEADs),China Energy Statistics Yearbook over the years,ChinaRegionalEconomicStatisticsYearbookand various provincial statistical yearbooks.The specific meanings of each major variable are listed in Table 1 and the descriptive statistics of panel data are listed in Table 2.
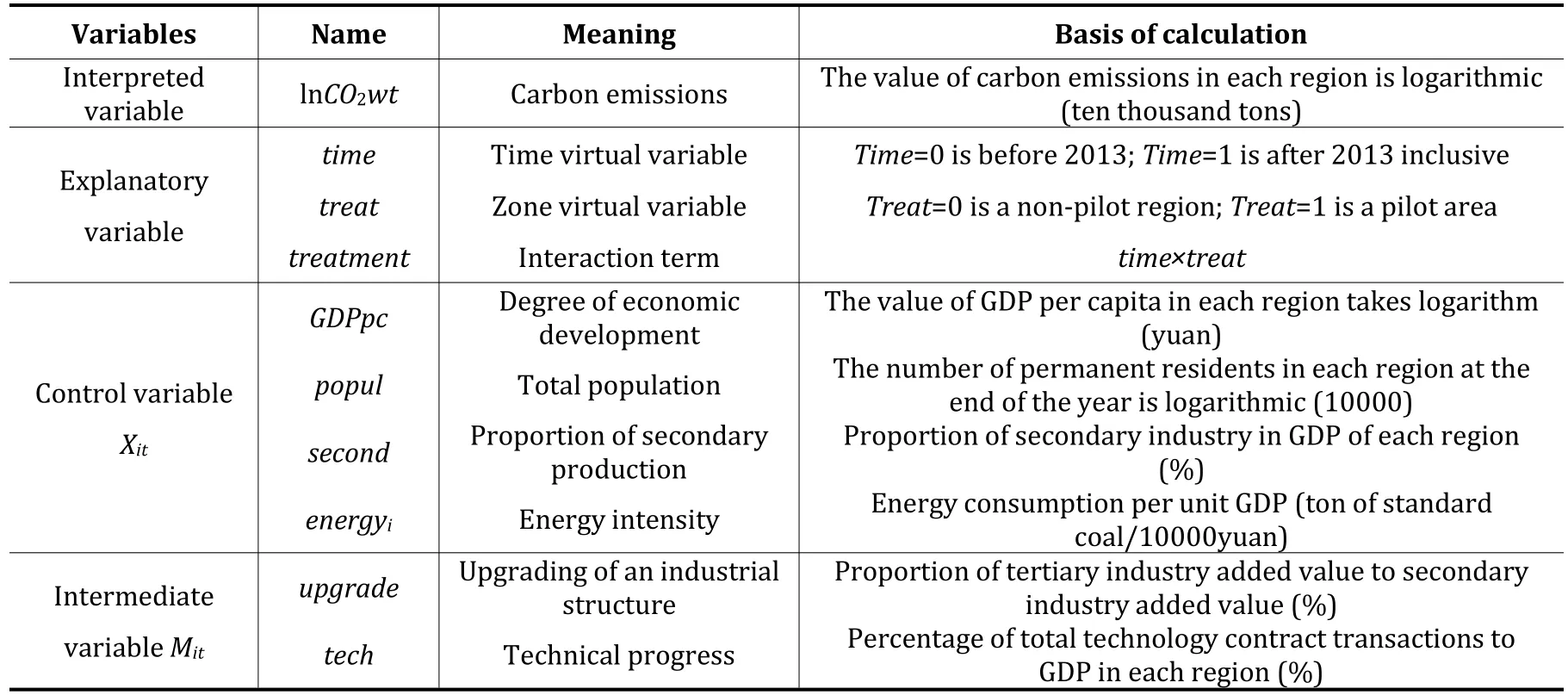
Table 1 Description of main variables

Table 2 Descriptive statistical results
4 Empirical analysis and robustness test
4.1 DID benchmark regression
Column (1) (2) in Table 3 shows the benchmark regression results of the dual difference model with and without control variables.It can be seen that the coefficient of treatment term is negative regardless of whether or not the control variables are added,and all are significant at the significance level of 5%,indicating that the implementation of the carbon emission trading policy can significantly reduce the CO2emission level in the pilot areas relative to the non-pilot areas.This shows that the pilot carbon emissions trading policy is effective,and the pilot carbon emissions trading policy has effectively reduced the carbon emissions in the pilot areas.

Table 3 DID regression results
4.2 Robustness test
4.2.1 Parallel trend test
The parallel trend assumes that the change trend of the treatment group and the control group before the event is the same,which is the key premise of double difference.The following model was thus constructed:
Among them,pre_4,pre_3,pre_2,current,post_1,post_2,post_3,post_4 and post_5 are all virtual variables,which represent the observed values in the first 4 years,the first 3 years,the first 2 years,the current year,the last 1 year,the last 2 years,the last 3 years,the last 4 years and the last 5 years of the implementation of the carbon emissions trading pilot policy.To avoid multicollinearity,delete the data from the year before the carbon trading pilot.The remaining variables are the same as the corresponding variables of the benchmark regression model.See Table 4 and Figure 1 for the regression results of the parallel trend test model.

Figure 1 Policy dynamics
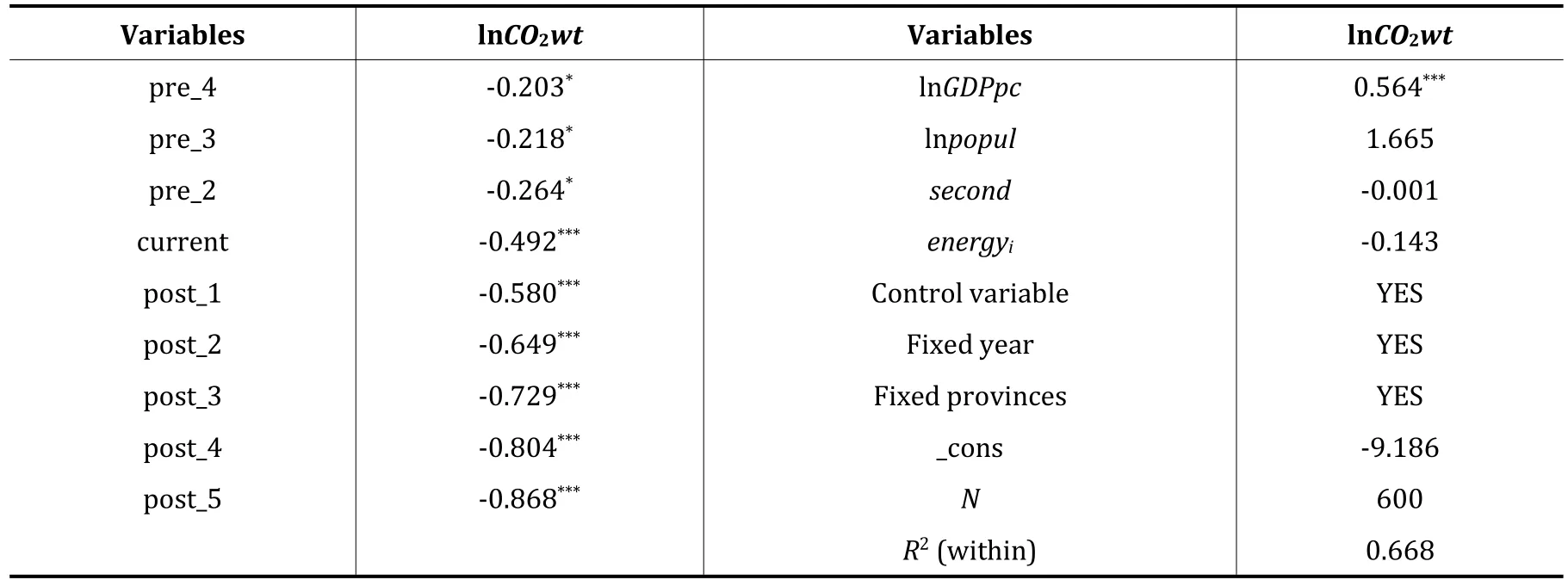
Table 4 Regression results of parallel trend test model
As can be seen from Table 4,the coefficients of PRE _4-PRE _2 did not pass the significance test of 5%,while both current and POST _ 1-POST _ 5 passed the significance test and were significant at the level of 1%.As can be seen from Figure 1,before 2013,the emission reduction effect of carbon trading policy was not significant,and after 2013,the emission reduction effect of carbon trading policy was significantly negative at the level of 5%.Table 4 and Figure 1 illustrate that the change trend of the carbon dioxide emissions of the experimental group and the control group before the implementation of the policy is the same,the assumption of parallel trend is satisfied,and the carbon emission reduction effect is achieved for the pilot area in the year of the implementation of the policy,and the carbon emission reduction effect is strengthened with the passage of time.Therefore,it is feasible to use the double difference method for estimation.
4.2.2 PSM-DID
Considering the selection bias between the treatment group and the control group,the propensity score matching method (PSM) was used to perform the neighbor 1: 1 matching to eliminate the selection bias between the treatment group and the control group as much as possible,and then the double difference model was used for analysis.Using the degree of economic development,total population,ratio of secondary production and energy intensity as indicators to compare whether the experimental group and the control group have homogeneity,the logit model was adopted to delete 431 samples that do not meet the matching criteria,and 169 observed values are obtained.
Table 5 shows that the treatment term coefficient is negative regardless of whether a control variable is added.After adding the control variable,the coefficient of treatment term is significant at the level of 5%.The results of double difference test for the samples with matching propensity score show that the carbon emission trading policy can effectively reduce the CO2emissions in the pilot areas.This is consistent with the benchmark regression conclusion of DID model in the previous part.

Table 5 PSM-DID regression results
As can be seen from Table 6 and Figure 2,the p value of each variable after matching is greater than 0.05 after the propensity score matching,and the standard deviation of the control variable of the sample is effectively reduced after matching.Therefore,it can be considered that the effect of propensity score matching is better.

Figure 2 Standard deviation of control variables before and after matching

Table 6 PSM balance test results
4.2.3 Placebo test
In order to further test whether the research conclusions in this paper may be caused by other unobservable factors,this paper conducted a placebo test by randomly sampling the experimental group.The results of the placebo test are shown in Figure 3,in which the probability density distribution of the estimation coefficient and its p value are reported.The placebo test was repeated the random process 500 times,resulting in 500 coefficient estimates.From the figure,it can be seen that the coefficient estimates are concentrated in the vicinity of zero and approximately follow the normal distribution,and the p value is mostly greater than 0.1,which is not significant.The dashed red line perpendicular to theXaxis indicates the true coefficient values,which are significantly different from the distribution of the randomly generated coefficient estimates,indicating that the true coefficient values are not due to other unobservable factors.In other words,the randomly generated carbon emission right pilot areas have no emission reduction effect,and the carbon emission reduction effect of the carbon emission right pilot on the experimental group is real,which verifies the robustness of the benchmark regression conclusion in this paper.

Figure 3 Diagram of placebo test results
5 Mechanism test of emission reduction effect
In order to explore the impact mechanism of carbon emission reduction in pilot areas,this paper uses the method of intermediate effect test to study the carbon emission reduction mechanism.The intermediate variables include industrial structure upgrading and technological progress.There is no doubt that upgrading the industrial structure and technological progress are the core ways to reduce carbon emissions.
This paper used stepwise regression method,sobel test method and bootstrap test method to test the mediating effect of two mediating variables.
In order to test the intermediate effect,the following three equations were constructed:Mit is the intermediate variable,the coefficient C represents the total effect of the implementation of the policy on carbon emissions,the coefficient A represents the effect of the implementation of the policy on the intermediate variable,the coefficient B represents the effect of the intermediate variable on carbon emission reduction,the intermediate effect is the product of the coefficient A and the coefficient B,and the coefficient C’represents the direct effect of the intermediate variable on carbon emission reduction.Other variables in the model have the same meanings as the corresponding variables in the benchmark regression model.
Referring to the research of Wen and Ye(2004),the three-step method was used to test the mediating effect.If the coefficients A and B are both significant,the mediating effect exists;otherwise,the sobel test is required.If the p value of the sobel test is less than 0.1,the mediating effect exists;otherwise,the mediating effect does not exist.
5.1 Stepwise regression method
The results of stepwise regression are shown in Table 7.For the test of the mediating effect of industrial structure upgrading,the treatment coefficient in column (1) is significantly negative at 1%.This indicates that the carbon trading policy will reduce the carbon emissions in the pilot areas.In other words,the total effect of stepwise regression is significantly negative.

Table 7 Stepwise regression results
The treatment coefficient in column (2) is significantly positive at the level of 5%,indicating that the carbon emissions trading will cause the upgrading of the industrial structure in the pilot areas.The pilot areas are facing the pressure of emission reduction and carbon reduction,accelerating the development of high-tech enterprises and low-carbon technology enterprises,and promoting the upgrading and adjustment of the regional industrial structure.The treatment coefficient of column(3)is significantly negative at the level of 1%,and the coefficient of industrial structure upgrading is also significantly negative at the level of 5%,indicating that the industrial structure upgrading plays a part of intermediary role in the regional carbon emission reduction effect,and the carbon emission right transaction increases the carbon emission cost of emission control enterprises and causes the regional industrial structure upgrading to reduce the carbon emission in the pilot region.
For the test of the mediating effect of technological progress,the treatment coefficient of column (4) is positive but not significant,while the tech coefficient of column (5) is significantly negative at the level of 5%,and the treatment coefficient of column(5)is significantly negative at the level of 1%,thus the stepwise regression test of technological progress is stopped.In view of the fact that the assumption of stepwise regression is the stronger of the mediating effect test methods,the mediating effect test of the remaining two more general methods is carried out instead.
5.2 Sobel test
As can be seen from Table 8,the sobel test conducted after controlling the regional and time effects shows that the p value corresponding to the intermediate effect of industrial structure upgrading and technological progress is significantly less than 0.01,and it is significant at the level of 1% of the sobel value.The sobel intermediate effect test passes,i.e.the industrial structure upgrading and technological progress play a significant intermediate effect in the impact of carbon emissions trading on carbon dioxide emissions.And the direct effect of the implementation of carbon emissions trading policy is significant in both models,further verifying that the implementation of carbon emissions trading policy effectively reduces carbon emissions in pilot areas.

Table 8 Sobel test results
5.3 Bootstrap test
In the bootstrap test of controlling regional and time effects(Table 9),the confidence interval of the intermediate effect and the confidence interval of deviation correction do not include 0 when the confidence level of industrial structure upgrading and technological progress is 95%,and the bootstrap test passes.In other words,the upgrading of industrial structure and technological progress play a significant mediating role in the impact of carbon emissions trading on reducing carbon dioxide emissions,and the direct effect of carbon emissions trading policy implementation is significant in both models,which is consistent with the conclusion of Sobel test method.

Table 9 Bootstrap test results
In conclusion,due to the strong assumption of stepwise regression test,the intermediate effect test of the intermediate variable of industrial structure upgrading passed the test,while the intermediate effect test of the intermediate variable of technological progress failed the test.Through the more universal sobel intermediate effect test and bootstrap intermediate test,the conclusion is that the carbon emissions trading reduces the carbon dioxide emissions of the pilot provinces and cities through the upgrading of industrial structure and technological progress.
6 Conclusions and policy recommendations
6.1 Conclusions
Based on the panel data of 30 provinces,autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government in China from 2000 to 2019,this paper uses the double difference method to explore the carbon emission reduction effect of the carbon emission trading pilot policy,and analyzes the impact mechanism of the carbon emission reduction effect of the carbon emission trading pilot policy through the intermediate effect test.The research shows that:
First,compared with non-pilot areas,the carbon emission trading pilot policy significantly promotes the carbon emission reduction in the pilot areas.Moreover,the conclusion drawn from the benchmark regression is robust and has been verified by the propensity score matching double difference model,parallel trend test and placebo test.And the effect of carbon emission reduction is increasing year by year.
Second,the stepwise regression method,sobel test method and bootstrap method of intermediate effect test all indicate that the carbon trading pilot policy reduces the carbon dioxide emissions in the pilot areas by promoting the intermediate variable of industrial structure upgrading.
Third,because the hypothesis of stepwise regression test is too strong,the intermediate effect test of technological progress,an intermediate variable,fails.However,the more universal sobel test and bootstrap test show that the carbon trading pilot policy reduces the carbon dioxide emissions in the pilot areas by promoting technological progress as an intermediate variable.
6.2 Policy recommendations
Based on the above research conclusions,this paper puts forward the following policy recommendations:
First,improve the establishment of a unified national carbon market and the construction of a market mechanism,use economic policies to stimulate low-carbon transformation,and carry out financial,tax and price policy incentives for projects such as low-carbon products.Introduce green credit,bonds and other products,promote the concept of responsible investment to provide financing for environmentally friendly,socially responsible and good corporate governance (ESG)companies,and promote climate-related financial risk prevention and regulatory innovation while benchmarking international green finance.
Second,speed up the improvement of the relevant trading legislation in the carbon emission rights market.Accelerate the expansion of the national carbon emissions trading coverage industry,and include the thermal,cement,petrochemical and other heavy emission industries into the trading market coverage.Adhere to the principle of“common but differentiated“,fully consider the differences in economic level,development stage and resource endowments of different regions,design different standards for key emission units in different regions,and construct differentiated inclusion standards under overall fairness.Formulate scientific and effective punishment measures.
Third,plan the energy transformation plan,adjust the production and lifestyle,formulate the development path of industrial optimization structure,and speed up the research and development of low-carbon science and technology.In energy production,reduce the proportion of coal consumption,develop nuclear power safely,and develop renewable energy such as hydropower,wind power,solar energy,biomass energy and non-fossil energy for power generation.Vigorously develop low-carbon,zero-carbon,negative-carbon technologies with low cost,high efficiency,significant emission reduction and safety,and develop deep decarburization technologies such as hydrogen energy.
Acknowledgments
This paper is supported by the National Social Science Fund of China(Grant No.19CJY046).
- Ecological Economy的其它文章
- Spatial and temporal heterogeneity of the impact of per capita income on household indirect carbon emissions in western China
- Structural characteristics and influencing factors of spatial correlation network for regional high-quality development in China
- Determinates of the competitiveness of provincial forest health care industry in China
- NDVI characteristics and precipitation sensitivity of urban agglomeration in Central Shanxi Basin
- Assessing the impact of manufacturing agglomeration on environmental pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region using spatial panel data model
- Guide to Authors

