Effect of auricular acupressure nursing on anxiety in patients with acute coronary syndrome
Xin-Yi Kong,Jie Li*
1Department of Cardiovascular Intervention Room,The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University,Nanchang,China.
2Department of Internal Medicine,Jiangxi Chest Hospital,Nanchang,China.
Abstract Objective: To explore the effect of auricular acupressure nursing on the relief of anxiety after aortic balloon counterpulsation implantation in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS).Methods:From June 2018 to August 2021, 160 ACS patients who met the inclusion criteria in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University were selected and divided into the control group and experimental group according to the random number table method, with 80 cases in each group. The control group received comprehensive management of psychological stress management and sham procedure.The experimental group was treated with routine psychological stress management and auricular acupressure nursing. Patient anxiety scores were compared before and after nursing.Results:A total of 150 participants completed the study.There was no significant difference in the anxiety score between the two groups of patients before the intervention (P >0.05). After the intervention, the anxiety scores of the two groups were lower and statistically significant (P <0.05).The scores of moderate and severe anxiety were significantly better than those of the control group, the difference was statistically significant (P <0.05); but in the subgroup of mild anxiety,the two groups were not statistically significant(P >0.05). The clinical efficacy of the two groups was compared with that of the experimental group. The three subgroups (Unstable angina,Non ST segment elevation myocardial infarction, Segment elevation myocardial infarction) in the experimental group were significantly lower than those before the intervention, which was statistically significant (P <0.05).Conclusion: Auricular acupressure nursing can significantly reduce the anxiety of patients with ACS after aortic balloon counterpulsation implantation.
Keywords:Auricular acupressure, Acute coronary syndrome, Anxiety, Hamilton anxiety scale
Background
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is a group of clinical syndromes whose pathological basis is the rupture or invasion of coronary atherosclerotic plaque followed by complete or incomplete occlusive thrombosis. It is currently a threat to human health [1].Intra-Aortic-Balloon-Pump (IABP) is one of the most widely used mechanical circulatory assist devices for ACS patients. When uncontrollable low cardiac output syndrome occurs,the application of IABP can effectively improve myocardial blood supply and oxygen supply [2]. However, low cardiac output syndrome often presents with abrupt onset and rapid disease progression, whicn causes psychological fluctuations in the patient with IABP. To a certain extent, they are prone to negative emotions such as anxiety, which have adverse effects on prognosis [3]. Therefore, early psychological intervention for patients with IABP is of great significance to help them pass through the dangerous period. Auricular acupressure nursing is a long-standing treatment in traditional Chinese medicine technique. Auricular acupressure was performed by using acupressure seeds named "Seeds of Wangbuliuxing". The seeds were kept in place by a piece of opaque adhesive patch and fixed onto the acupoints selected. Some studies showed that auricular acupressure can relieve anxiety [4, 5]. This study aims to investigate the effect of auricular acupressure on postoperative anxiety patients after ACS.
Methods
A total of 160 ACS patients were recruited in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University from June 2018 to August 2021.Patients who met the inclusion criteria were divided into experimental group and control group using the random number table method,with 80 cases in each group. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University(NO. 69), and all patients gave informed consent.
Inclusion criteria included (a) meeting the diagnostic criteria for ACS [6]; (b) undergoing IABP; (c) not receiving traditional Chinese medicine treatment within the past 1 month. The exclusion criteria included (a) unconsciousness and history of mental illness; (b)pregnant and lactating women; (c) allergic constitution; (d)participated in other clinical trials in the past 1 month.
Interventions
The experimental group adopted routine psychological stress management and auricular acupressure nursing. Three standardised acupressure points were selected on the external ear according to the usual tenets of Chinese medicine and clinical experience: Shenmen(TF4), Sympathetic nerve (AH6a) and Subcortex (AT4). Ear pressing plasters (Wangbuliuxing seeds, purchased from Shandong Huayi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd) were applied to above points on both ears in each treatment (Figure 1)

Figure 1 Seeds of Wangbuliuxing
Auricular acupressure operation steps.The patient was asked to sit upright and the operator used a probe stick to press on the corresponding points in the ear to find the corresponding points required for the intervention. After finding the points, sterilising the points with 75%alcohol preparation pads and left to dry,the operator applied the ear pressing plaster with the seed at the acupoints (Figure 2). Patients were instructed to press the ear seeds 2-3 times a day by themselves for 2-3 minutes each time, and massage again for 30 minutes before going to bed at night to the extent that the patient felt heat, swelling, and slight pain. Thee ear seeds were replaced every 3 days for 1 weeks as a course of treatment, with timely subsidies in between if they fall out. All participants were observed whether the patient has symptoms such as fever and allergy. No damage and short-term adverse effects were reported.

Figure 2 Auricular acupressure operation
The control group was treated with comprehensive care of psychological stress management and placebo ear pressing plasters.The control group received sham auricular acupressure using placebo ear plasters without seeds (composed of dextrin, caramel powder,starch). The appearance and weight is same as the experimental group. The treatment procedure was the same as in the case group.
Anxiety score
Hamilton anxiety scale (HAMA) [7] is adopted to assess remission of anxiety. The scale contains 14 items including anxiety, tension, fear,insomnia, cognitive function, depressive mood, somatic anxiety(muscle system and sensory system) cardiovascular symptoms,respiratory symptoms, gastrointestinal symptoms, genitourinary symptoms,autonomic nervous system symptoms, and behavior during talks.Combination of conversation and observation was used to assess the patient's subjective experience. The score is from 0(no symptoms)to 4 (extremely severe). 1 indicates no symptoms; 2 indicates that there are certain symptoms, but does not affect social function; 3 indicates that the symptoms are severe and require additional treatment, or have affected life and activities; 4 indicates that the symptoms are extremely severe and seriously affect social functions.A score of ≥14 and <21 was considered mild anxiety, a score of ≥21 and <29 was considered moderate anxiety, and a score of ≥29 was considered severe anxiety.
Criteria for determining clinical efficacy
Referring to "Guidelines for Clinical Research of New Chinese Medicines" [8], clinical control refers to the disappearance of emotional symptoms (tension, fear, anxiety) and physical symptoms(dry mouth, frequent urination, urgency, sweating, tremor,restlessness, restlessness). Significant effect refers to the significant reduction of emotional and physical symptoms. Effective refers to the reduction of emotional and physical symptoms. Ineffective refers to the lack of relief of emotional and physical symptoms.
Statistical Analysis
SPSS 23.0 statistical software was used for data analysis. The categorical data was analyzed using Pearson χ2tests or Fisher’s exact tests. Paired t tests were used to compare related samples and independent t tests were used to compare independent samples.Results are presented as mean ± SD.P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
A total of 150 participants completed the study while 10 participants withdrew from the study for many different reasons and their data are not included in the final analysis. In the control group, 4 cases were dropped out during the nursing intervention, and finally 76 cases completed the treatment. 6 patients in the experimental group were dropped out during the nursing intervention, and finally 74 cases completed the treatment. The characteristics of 150 participants are shown in Table 1. There was no significant difference in gender (χ2=1.78) and age(t=2.45) between the two groups(P>0.05).There was no significant difference in anxiety scores between the two groups before nursing intervention (P>0.05). After nursing intervention,the anxiety scores of the two groups were both decreased and statistically significant(P<0.05).The scores of post-moderate and severe anxiety in experimental group were significantly better than those of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05) as shown in Table 2. The clinical efficacy of the experimental group was better than that of the control group as is shown in Table 3.
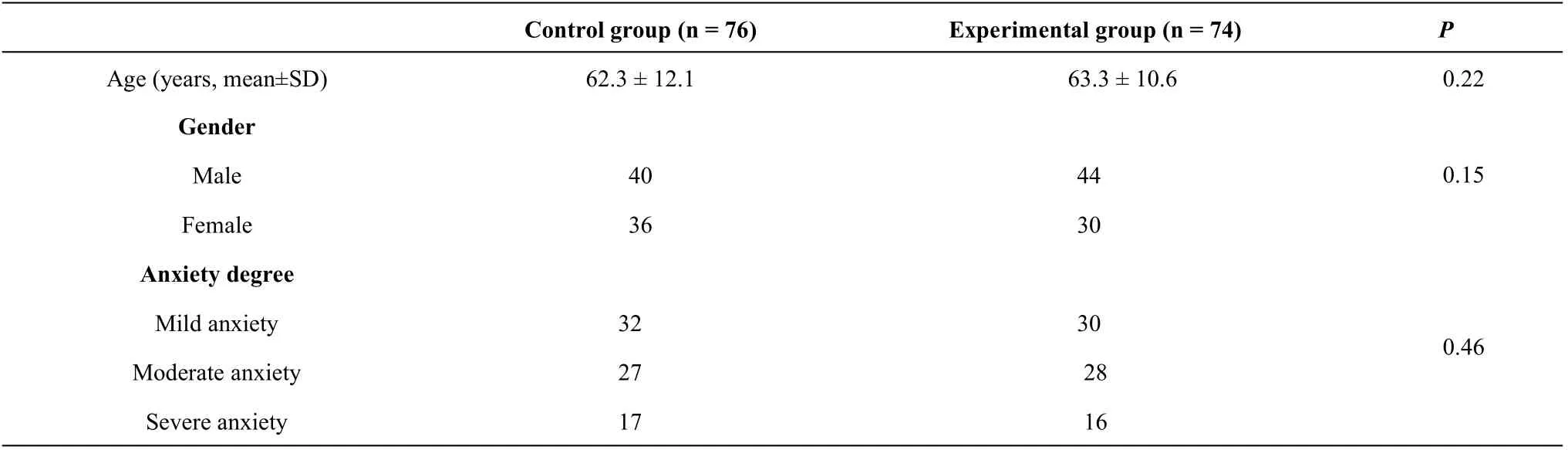
Table 1 Demographic characteristics at baseline
ACS is divided into three subgroups: unstable angina (UA),non-st-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), and st-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). Comparison of anxiety scores before and after treatment in different types of patients in the experimental group, after the nursing intervention, the three subgroups were significantly lower than those before the intervention,with statistical significance (P<0.001), but the STEMI group was still in a state of moderate anxiety after the intervention (Table 4).

Table 2 Comparison of anxiety scores before and after nursing intervention in two groups(mean±SD)

Table 3 Comparison of clinical efficacy between two groups

Table 4 Comparison of anxiety scores of subgroups in the experimental group
Discussion
Traditional Chinese medicine believes that "the twelve meridians lead to the ear"and"the ear is the gathering of the main veins".Each organ of the human body has a corresponding representative area on the auricle, and is regularly distributed on the auricular points [4]. This study selects Shenmen(TF4),sympathetic nerve(AH6a)and subcortex(AT4). The choice was based on the meridian theory of traditional Chinese medicine with a sedative mechanism to regulate cortical excitation and inhibit brain function. Among them, the subcortex(AT4)is the key point for regulating the function of the cerebral cortex,which can nourish the marrow and benefit the brain, relieve pain and soothe the nerves, and treat insomnia and dreams. Shenmen (TF4) is the key point for regulating the excitation and inhibition of the cerebral cortex, which can regulate the function of the cerebral cortex and play a role in nourishing the blood and calming the mind.Stimulation of the Shenmen point can produce a calming effect on participants and can be used as sedation. Sympathetic nerve (AH6a)acupoints regulates the function of autonomic nerves, and have the effects of relaxing tendons and activating collaterals, calming the heart and soothing the nerves[5].
This study showed that the anxiety state of patients with mild,moderate and severe anxiety in the experimental group was significantly relieved after 1 week of auricular acupressure nursing,which was similar to Ni's observation on the anxiety state of patients during the perioperative period [4]. Similar observations were made for anxiety states in perioperative patients.Surgery is a strong stressor for patients. Auricular acupressure stimulation will increase the secretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine through sympathetic nerves, aggravating the patient's mental stress and changes in psychological behavior [9]. Auricular acupressure stimulates the acupuncture points on the auricle and regulates the meridians,thereby regulating the mind, calming the mind, enabling the smooth recovery of ACS patients and reducing the adverse reactions of surgical treatment.
For patients with moderate anxiety, although both groups of patients were significantly improved after nursing intervention, the effect of the experimental group was better than that of the control group (P<0.001); for patients with severe anxiety, the control group had no significant effect after intervention (P>0.05), but the experimental group had obvious advantages. The reason may be that moderate and severe anxiety is partially irreversible. Traditional nursing methods mainly focus on psychological counseling. It takes a long time to establish the effect of psychological counseling, and it is difficult to effectively relieve it within a week. Auricular acupressure improves anxiety. On the other hand, nurses can better communicate with patients while pressing acupoints, making health education smoother, making patients feel more secure, further relieving patients’nervousness to a certain extent, and improving treatment effect [11].Among the clinical types of coronary heart disease, ACS patients are prone to have severe psychological symptoms, and anxiety is one of the common manifestations. Several studies [3, 12, 13] have shown that anxiety can aggravate the poor prognosis of ACS, and there is a positive correlation between the two [14]. Therefore, timely improvement of anxiety symptoms is of great benefit to alleviating ACS.
This study shows that in the three subgroups of ACS, after auricular acupressure, the patients in the UA and NSTEMI groups were freed from the anxiety state; although the STEMI group had a lower score than before, they were still in a moderate anxiety state. On the one hand, the patient's own symptoms are severe, the psychological expectation gap before and after treatment is large, and the anxiety state lasts for a long time [15-17]. On the other hand, it may also be related to the shorter observation time, because the advantage of traditional Chinese medicine lies in its long-term effects.
In terms of the total effective rate, the experimental group is significantly better than the control group, which may benefit from the theoretical essence of the "holistic concept" of Chinese medicine,indicating that auricular acupressure has the functions of dredging meridians, regulating nerves, regulating Qi and blood, and balancing endocrine.
The limit is our study is a single-center study, the sample size is small and the observation period is short.It is hoped that the next step will be to include a larger sample to observe for a longer period of time and to explore the underlying mechanism of action if necessary.
Conclusion
Auricular acupressure nursing can significantly reduce postoperative anxiety state of ACS patients, especially for postoperative and moderate and severe anxiety state of UA and NSTEMI. Auricular acupressure has low cost and minimal side effects, which is helpful for patients to cooperate with clinical treatment.

