Transcriptome analysis reveals immune-related genes in tissues of Vibrio anguillarum-infected turbot Scophthalmus maximus*
Yuting SONG, Maqsood Ahmed SOOMRO, Xianzhi DONG, Guobin HU,**
1 College of Marine Life Sciences, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266003, China
2 Institute of Evolution & Marine Biodiversity, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266003, China
3 Institute of Biophysis, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
Abstract Turbot Scophthalmus maximus is an important mariculture fish species with high economic value. However, the bacterial diseases caused by Vibrio anguillarum infection bring huge economic losses to the turbot aquaculture industry.To understand the immune response of the turbot against V. anguillarum infection and to explore novel immune-related genes, the transcriptome analysis of turbot spleen and gills were conducted after V. anguillarum infection.Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified in spleen and gill of the turbot amounted to 17 261 and 16 436, respectively.A large number of immunerelated DEGs were enriched in cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction signaling pathway, and the others by the kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) enrichment.The gene ontology (GO)classification analysis revealed that V. anguillarum infection had the greatest effect on biological processes and cellular components.Twelve immune-related DEGs were identified in the spleen (cstl.1, egfl6, lamb21, v2rx4,calcr, and gpr78a) and gills (ghra, sh3gl2a, cst12, inhbaa, cxcl8, and il-1b) by heat map.The proteinprotein interaction (PPI) networks were constructed to analyze the immune mechanism.The results demonstrate that the maturation and antigen processing of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecule, and calcitonin- or adrenomedullin-regulated physiological activity were important events in the immunity of turbot against V. anguillarum infection.In the gills, the protein interactions in TGF-β signaling pathway, production of inflammatory factors, and endocytosis regulation were most significant.Our research laid a foundation for discovering novel immune-related genes and enriching the knowledge of immune mechanisms of turbot against V. anguillarum infection.
Keyword: Scophthalmus maximus; Vibrio anguillarum; transcriptome; differentially expressed genes;immune mechanism
1 INTRODUCTION
Scophthalmus maximus(Linnaeus, 1758) is a species of marine flatfish that is naturally distributed along the coastal regions of Europe.Turbot gained popularity mainly for its taste and nutritive value.Owing to this, the consumption of turbot in Europe and China still has an increasing trend against the backdrop of high production costs.In order to meet the consumption demand, large-scale turbot farming has been accomplished in Europe (Fernández-González et al., 2021).In 1992, Professor Jilin LEI and his colleagues at the Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute in Qingdao, China, brought juvenile turbot from the United Kingdom to China.In 1999, the commercial-scale juvenile production began in the Shandong province of China and then expanded to become the world’s largest producer of farmed turbot(S.maximus) marked the dawn of a new era in flatfish farming industry.The regions of turbot aquaculture are concentrated in Tianjin City, Liaoning,Hebei, Shandong, Jiangsu, and Fujian provinces, with Shandong Province contributing up to 49% of the total turbot production annually (Huang and Yang,2011).The development of fisheries not only creates a huge economic value, but also raises the economic income and improves the living standard of the population, especially for coastal areas.Nevertheless,the prevalence of disease caused byVibrio anguillarum(Bergman, 1909) infection remains a serious issue to turbot aquaculture.
Vibriosis is a major disease found among various coastal and brackish water fish species and is triggered by several types ofVibrio.V.anguillarumis a gram-negative, halophili, rod-shaped with polar flagella bacterium that has been found in over 20 marine fish species, including turbot (Guanhua et al., 2018).V.anguillaruminfection can trigger fatal septicemia hemorrhagic disease, and such infectious diseases pose one of the most significant threats to successful aquaculture and larviculture (Frans et al.,2011).The widespread ofVibriospecies in cultured marine organisms has been a serious concern of the aquaculture sector (Pujalte et al., 2003; Tan et al.,2015).Such threats from pathogens result in an unanticipated future for the aquaculture industry’s economic viability due to the intensification of aquaculture activities.Owing to the above issues, it is extremely important to investigate the immune responses of fish against different pathogens to minimize the spread of diseases in fish aquaculture(Mutz et al., 2013).
In recent years, RNA-Seq has been applied by many researchers to elaborate diseases triggered by pathogens and the defense mechanisms (Morozova et al., 2009).In particular, it also represents the host immune mechanisms that are effective against pathogen and demonstrates how the pathogen overcomes hostmediated immune responses (Kroeker et al., 2012).In addition, it has also been used to explore the molecular mechanisms of the host immune response after vaccination, such as inactivatedAeromonas salmonicida(Emmerich and Weibel, 1984) andVibrio scophthalmi(Cerdà-Cuéllar et al., 1997) vaccine(Xue et al., 2021a; Xiu et al., 2022).Several studies related to immune responses of turbot to viral infection and bacterialinfection have been performed by RNA sequencing (Pereiro et al., 2012; Robledo et al.,2014; Ronza et al., 2019; Librán-Pérez et al., 2022).
The spleen is the primary filter of blood-borne antigens and serves as an immunopoietic organ.The gills of fish have not only non-specific immune functions but also specific immune response functions and they are the first to contact with the external environment or pathogens when they invade under natural conditions (Dalmo et al., 1997).Therefore,the spleen and gills are the target organs to study the immune response of turbot against viral and bacterial infections.For example, Xue et al.(2021b) has suggested that non-coding RNAs (ncRNA) may regulate the expression of immune-related genes in the immune response of turbot spleen afterA.salmonicidainfection.In addition, the transcriptome analysis of turbot gills was performed to investigate the mechanism of physiological changes during waterless transportation(Nie et al., 2020).In addition, the intestine miRNA transcriptome of turbot has also been conducted afterV.anguillaruminfection (Gao et al., 2019).We utilized RNA-Seq to elucidate the immune mechanism of turbot toV.anguillarumbacterial infection targeting at the spleen and gills tissues, analyzed the transcriptome gene expression, and explored the regulation in signaling pathways.Our aim is to provide a new source of genetic information and to broaden our understanding on turbot immune regulatory mechanism that can be used in future on the immunological response ofV.anguillaruminfection.
2 MATERIAL AND METHOD
2.1 Fish and V. anguillarum strain
Live turbot (mean weight 1 000±50 g,n=6) were purchased from the local fish market in Qingdao City, Shandong Province, China.Six turbots were acclimated at 22±2 °C for two weeks of temporary breeding.V.anguillarum,provided by Prof.Xiaohua ZHANG (Ocean University of China, Qingdao,China) was kept stored in glycerol (30%) at -80 °C.The fish were divided into two groups, where those injected withV.anguillarumsuspension were considered as experimental group (n=3) and the individuals injected with isopyknic phosphoric acid buffer solution (PBS) (Sigma-Aldrich, P3813) as control group (n=3).The concentration of viableV.anguillarumsuspension was 1×109CFU/kg body weight (Song et al., 2021a).Fishes in both groups were reared in seawater for 24 h, and mild symptom of ascites was observed in all the turbots of experimental group.All fish were euthanized using 100-mg/L ethyl 3-amino-benzoate-methanesulfonic acid (MS-222) (Sigma-Aldrich, E10505) for 30 min to separate the spleen and gills.
2.2 Total RNA extraction, library construction,and transcriptome sequencing
The spleen and gill tissues (mean weight 1±0.1 g)were aseptically collected into clean Eppendorf (EP)tubes containing 1-mL RNAiso Plus (TaKaRa,(TaKaRa, Japan)).Samples of each group were mixed together for total RNA extraction.All steps involving RNA extraction were carried out following the protocol described in the instruction manual of“RNAiso Plus”.The RNA concentration was measured using Nano-Drop 2000 spectrophotometer(Thermo, USA) and the integrity was evaluated by agarose gel (Biowest, 111860) electrophoresis.NEBNext?UltraTMRNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina?(NEB, USA) was used to construct the sequence library according to the guidelines of the manufacturer.The clustering of the index-coded samples was performed on a cBot Cluster Generation System using TruSeq PE Cluster Kit v3-cBot-HS(Illumina, PE-401-3001) and paired-end reads were generated by Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform(Illumina, CA, USA) (Fang et al., 2022).
2.3 Transcriptome assembly and annotation
The raw data obtained by sequencing contains a small number of reads with sequencing adapters or low sequencing quality.Fastp program was used to filter the raw data.It mainly includes removing reads with adapters and removing reads containing N (N means that the base information cannot be determined).At the same time, the Q30 and GC content calculations were performed on the clean data and the lowquality reads were removed.All subsequent analyses are high-quality analyses based on clean data.The reference genome data and genome annotation information of turbot can be downloaded online(http://feb2021.archive.ensembl.org/Scophthalmus_maximus/Info/Index) (Song et al., 2022).The position information of clean reads on the reference genome was obtained by constructing the index of the reference genome and aligning the clean reads with the reference genome through HISAT2 (version v2.0.5).
2.4 Differentially expressed genes (DEGs)identification, annotation and GO, and KEGG enrichment analysis
The results of the genome alignment were used to calculate the reads mapped to reference gene by featureCounts (version 1.5.0-p3).The fragments per kilobase of exon model per million mapped reads(FPKM) of each gene was calculated based on the length of the gene.The adjustedP-value (padj)lower than 0.05 and the |log2(fold change)|≥1 of the transcripts were considered to be the DEGs.Furthermore, the GO classification analysis and KEGG enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes were realized by R package clusterProfiler.
2.5 Bioinformatics analysis of immune-related DEGs
The results of KEGG enrichment analysis were used to screen immune-related DEGs (Li et al., 2020).Heat maps were used to visualize the abundance of DEGs in different tissues.Immune-related DEGs with high log2(fold change) were selected from the spleen and gills, respectively.Protein transmembrane structure,subcellular location, and signal peptides were predicted by TMHMM Server v.2.0 website, Cell-PLoc 2.0 website, and SignalP-5.0 Server website(Song et al., 2021b).Visualization of the proteinprotein interaction (PPI) network was using Cytoscape software (version 3.9.1).The interaction parameter of the immune-related DEGs with their interaction proteins was obtained through STRING database.
2.6 Quantitative polymerase chain reaction(qPCR) analysis
To validate the reliability of turbot spleen and gills transcriptome data, three genes with up-regulated fold change and three with down-regulated fold change were selected for qPCR verification (Li et al.,2020).The 5X All-In-One RT MasterMix Kit (with AccuRT Genomic DNA Removal) (ABM, G492) was used to remove gDNA and synthesize the first strand of cDNA (Song et al., 2022).The primer information of these six genes is shown in Supplementary Table S1.The gene expression levels of these six selected genes were normalized against the reference gene (β-actin)(Gao et al., 2020).The cDNA extracted from turbot spleen or gills was used as template and the BrightGreen 2X qPCR MasterMix reagent (ABM,10000218) was used to perform qPCR reaction with the SYBR?Green method of ABI 7500 fluorescent PCR instrument (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, USA).
3 RESULT
3.1 Transcriptome sequencing and identification and annotation of DEGs
The transcriptome sequencing statistics of four libraries are shown in Supplementary Table S2.Each library contained approximately 44 million raw reads and a large proportion of the clean reads were filtered from the raw data for subsequent analysis.The G/C content of each library ranged from 49.52%to 52.27% and the Q30 of each library was higher than 94%, suggesting that the sequencing data is of high quality.The number of DEGs identified in turbot spleen was 17 261, including 525 up-regulated and 177 down-regulated (Fig.1a).The DEGs in turbot gills were 16 436, including 1 009 up-regulated and 1 057 down-regulated, respectively (Fig.1b).The ratio of reads aligned to the exon region of the genome accounted for about 80% of the number of clean reads,which indicated that the annotation of the genome is relatively complete and the subsequent gene expression quantification can be performed (Fig.2).
3.2 GO and KEGG enrichment analysis
By GO analysis, DEGs were annotated into three gene ontology categories, including biological processes, cellular components, and molecular functions (Fig.3).In the biological process category,“fin morphogenesis” and “appendage morphogenesis”have a higher ratio in spleen and “response to biotic stimulus”, “response to external biotic stimulus” and“response to other organism” have a higher ratio in gills of turbot.In spleen and gills of turbot,“extracellular region” has a higher ratio in the category of cellular component.The KEGG enrichment analysis showed that the DEGs in the turbot spleen were significantly enriched into carbon metabolism and autophagy-animal (Fig.4a).In the gills of turbot, cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction,vascular smooth muscle construction, and AGERAGE signaling pathway were most significant and enriched a large amount of DEGs (Fig.4b).The signaling pathway of neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction and extracellular matrix (ECM) receptor interaction were significant in both tissues.
3.3 Analyze immune-related genes by heat map
Seven immune-related signaling pathways were enriched in the spleen of turbot via KEGG enrichment analysis (Supplementary Table S3).In the gills, eight immune-related signaling pathways were enriched(Supplementary Table S4).Heat maps were used to visualize the abundance of DEGs in these signaling pathways.Among them,gpr78a,ctsl.1,v2rx4were significantly up-regulated, andegfl6,lamb2l, andcalcrwere down-regulated in the spleen (Fig.5).cxcl8,inhbaa, andil-1bwere significantly up-regulated,andsh3gl2a,cts12, andghrawere down-regulated in the gills (Fig.6).
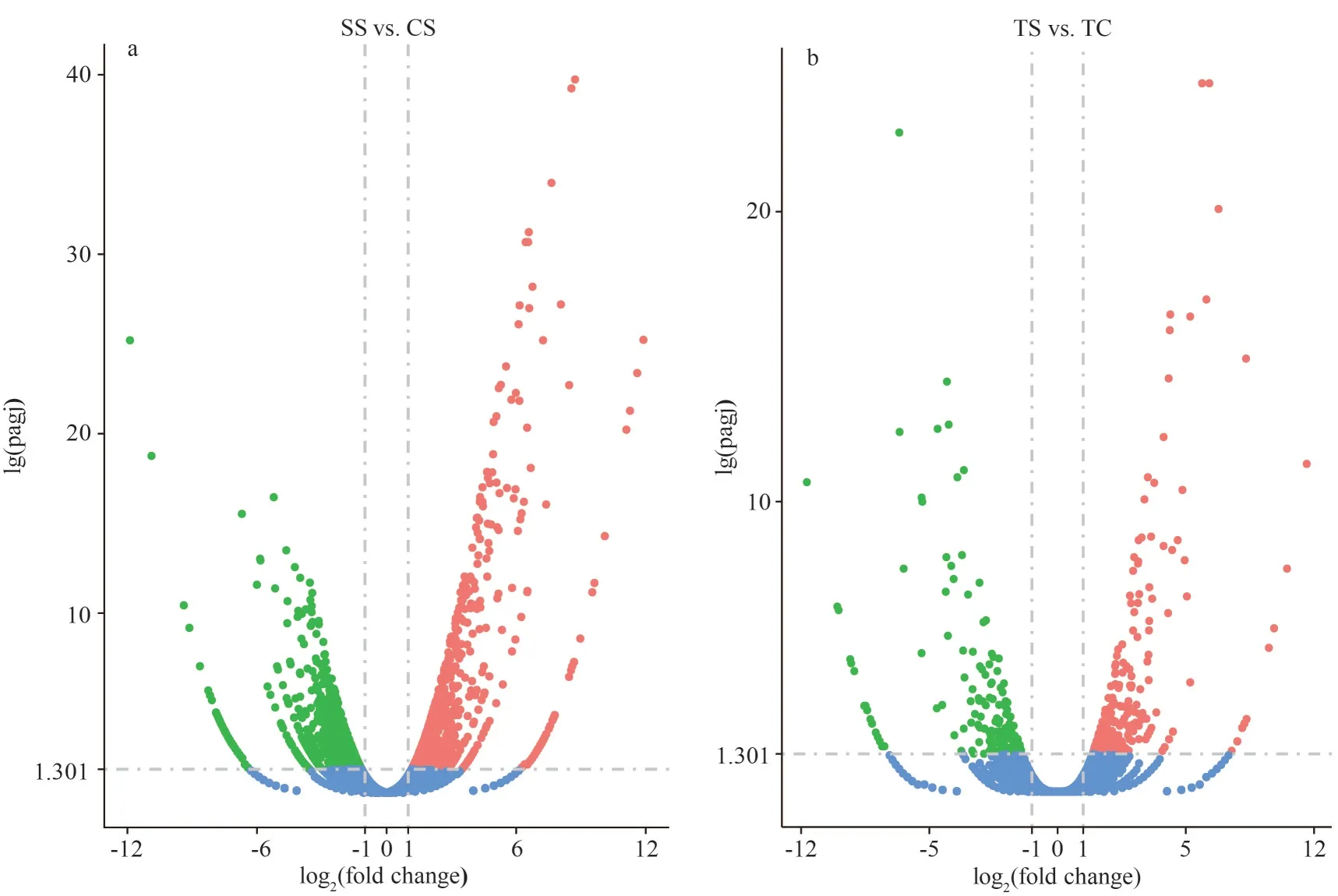
Fig.1 Volcano diagram of the DEGs of turbot gills (a) and spleen (b)

Fig.2 The distribution of sequencing reads in the genomic region

Fig.3 GO classification of DEGs of turbot spleen (a) and gills (b)
3.4 Bioinformatics analysis of interesting immune-related DEGs
All interesting DEGs,cstl.1,egfl6,lamb21,v2rx4,calcr,gpr78a,ghra,sh3gl2a,cst12,inhbaa,cxcl8,andil-1bexpressed in spleen or gills were analyzed by bioinformatics.The results of predicted transmembrane helices, signal peptides, and subcellular locations are shown in Table 1.In the spleen,lamb2landv2rx4are likely to function as extracellular signaling proteins.In gills, the possibility ofcts12,inhbaa, andcxcl8that may have a Sec signal peptide was high and their predicted subcellular locations were different, which indicates that the function location ofcxcl8andcts12is extracellular, whileinhbaais intracellular.Theghraandsh3gl2amay function as transmembrane proteins due to the high number transmembrane helices.
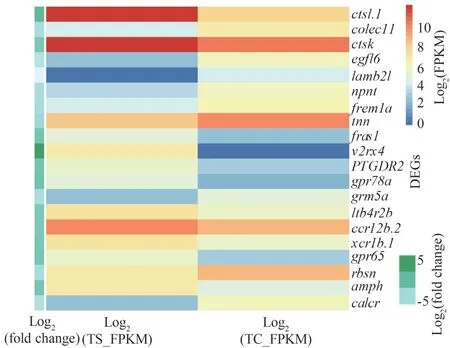
Fig.5 Heat map of the immune-related DEGs in the turbot spleen
3.5 PPI network construction of twelve immunerelated DEGs
Cytoscape software was used to realize the visualization of the PPI network.The PPI network ofcstl.1,calcr,egfl6,gpr78a,lamb21, andv2rx4in the spleen is shown in Fig.7.The PPI networks ofcst12,cxcl8,ghra,inhbaa,il-1b, andsh3gl2ain the gills are shown in Fig.8.Although there are interactions between these proteins, most of them are predicted based on text mining, phylogenetic co-occurrence or homology co-expression.Only a few interaction relationships were experimentally determined, such as ctsl.1-cd74a, calcr-calca, calcr-RAMP3, calcr-RAMP1, IL-1b-IL1RAP, inhbaa-acvr1c,inhbaa-acvr2bb, fstl3-inhbaa, sh3gl2a-amph, and sh3gl2a-synjl.The parameters of the experimentally determined interaction relationships are shown in Supplementary Table S5.Proteins with a higher score of experimentally determined interaction may play important role in the immune mechanism of turbot againstV.anguillaruminfection.
3.6 Prediction of immune mechanism in the spleen and gills of turbot

Fig.6 Heat map of the immune-related DEGs in the turbot gills
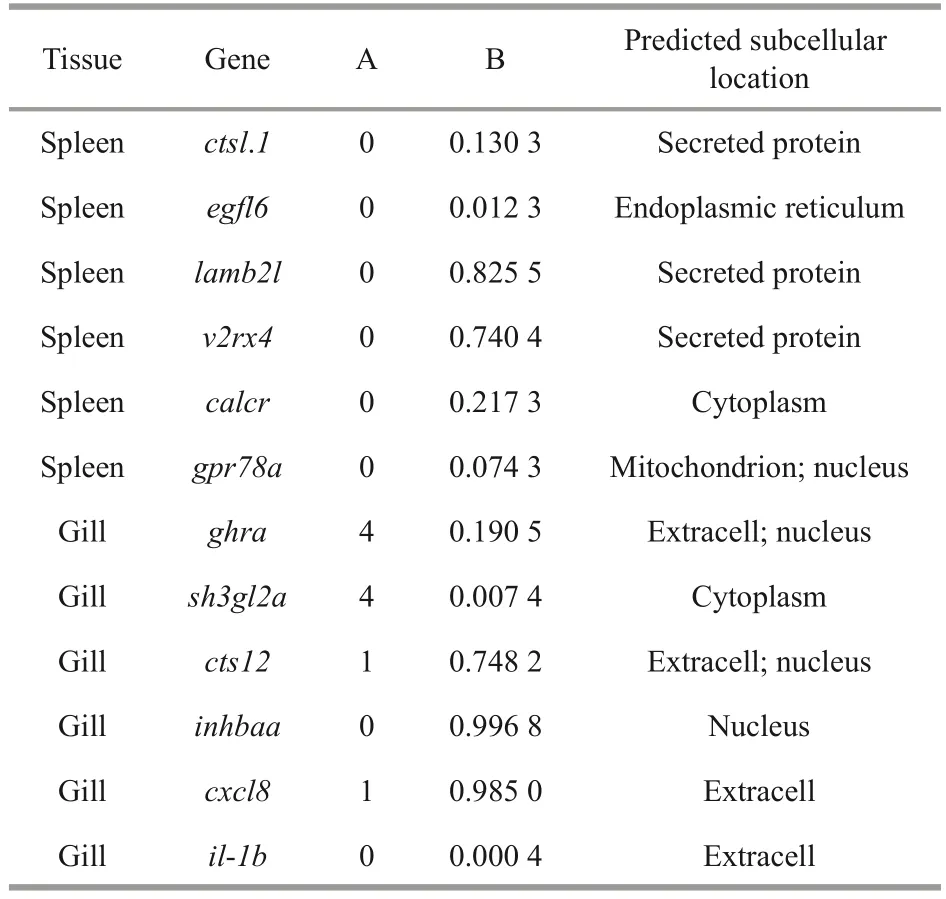
Table 1 Bioinformatics analysis of selected immunerelated DEGs
The prediction of the immune mechanism in the spleen and gill of turbot againstV.anguillaruminfection is based on the results of the above analysis (Fig.9).In gills, the complex formed by interleukin 1 receptor (IL-1R) and interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAP) interacts with interleukin 1 beta (IL-1b) involved in proinflammatory responses inV.anguillaruminfection.The complex formed by inhbaa and acvr2bb is involved in physiological activities regulated by the TGF-β signaling pathway together with fsta.The amph contains an SH3 binding site through which it is able to bind to the SH3 region on sh3gl2a.The synjl, a synaptic protein with phosphatidylinositol phosphatase activity, can bind to amph and sh3gl2a to regulate endocytosis.In spleen, the interaction of ctsl with CD74 plays an important role in degrading the invariant chain of MHC class II molecule and affects its function of antigen processing.The calcr associated with RAMP1 has high affinity for calca,whereas association with RAMP2 or RAMP3 results in higher affinity for adrenomedullin.
3.7 Validation of RNA-Seq data
Six immune-related DEGs,cstl.1,v2rx4,gpr78a,egfl6,lamb21, andcalcrwere selected to validate the accuracy of the RNA-seq data by qPCR.The expression levels of these DEGs showed similar log2(fold change) to the RNA-seq data as shown in Fig.10a.The high correlation between the RNA-seq data and qPCR data (R2=0.967 1) demonstrated that the transcriptome data was accurate (Fig.10b).
4 DISCUSSION
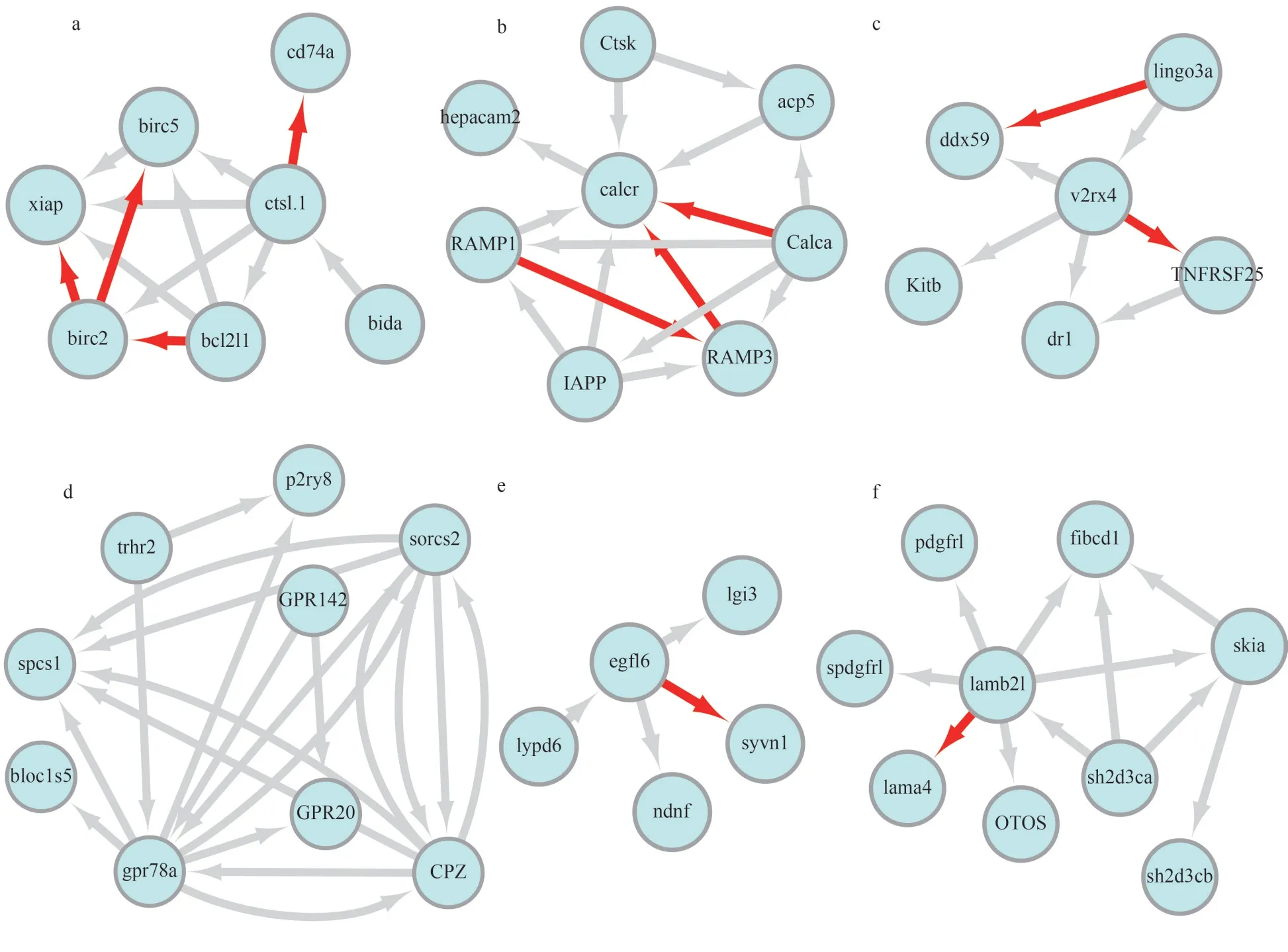
Fig.7 PPI Network of cstl.1 (a), calcr (b), v2rx4 (c), gpr78a (d), egfl6 (e), lamb21 (f) with other proteins in spleen of turbot
Fish farming, as the primary focus of aquaculture,has seen substantial growth across the globe in recent years (Li et al., 2015).However, numerous diseases induced by an intense farming paradigm are known to hinder the sustainable growth of fish farming.The absence of a successful revolutionary treatment for these fish diseases is largely due to a lack of indepth information on the immune response and pathogen resistance mechanisms (Jia et al., 2015;Zhu et al., 2015).Vibriosis is among the most commonly occurring aquatic animal bacterial infections, with heavy mortality rates all over the world (Estes et al., 2004; Xie et al., 2007).V.anguillaruminfection can cause hemorrhagic septicemia, ascites, and fin rot in turbot (Oisson et al., 1996).After dissection, inflammation in the intestine and punctate as well as diffuse hemorrhage in the internal organs and surrounding muscle tissue can be observed (Frans et al., 2011).The pathogenicity ofV.anguillarumin several fish species has been well studied.RNA-Seq has been applied to explore the treatment of pathogen-induced diseases and the defense mechanisms against these pathogens in fish.The emerging advances in fish immunology could lead to the development of effective methods for defense against fish diseases.Transcriptome profiling at the whole genome expression stage is a powerful tool for assessing immune function in an experimental model.Transcriptome research, for example, may uncover variations in gene expression patterns through tissue types and conditions (Karsi et al., 2002; Martin et al., 2002; Meijer et al., 2005).
The pathogenV.anguillarumwas studied using transcriptome analysis in this research.Functional enrichment has demonstrated that there are ample immune-related genes in the transcriptome.Clear awareness of these mechanisms and genes enables researchers to discover the molecular mechanisms of the fish immune systems and provide us a better understanding of disease prevention and treatment.The innate immune system plays an integral role in defending against infectious microbial pathogens.Many innate immune-related signaling pathways have been identified from turbot transcriptome analysis, such as cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction,Salmonellainfection, ECM receptor interaction, endocytosis,herpes simplex virus 1 infection, phagosome,neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, and toll-like receptor signaling pathway.As shown in Figs.5 & 6,the expression abundance of immune-related DEGs was observed, such asil-1b,cstl.1,egfl6,lamb21,v2rx4,calcr,gpr78a,ghra,sh3gl2a,cst12,inhbaa,andcxcl8.Among these immune-related DEGs, onlycxcl8andil-1bas interleukin family members have been reported to be associated with the bacterial infection of turbot (Chai et al., 2006; Hu et al.,2011).

The red arrows indicated that the interaction direction between the two proteins; the grey arrows indicate the interaction of two proteins that havenot been experimentally validated.

Fig.10 Validation of RNA-seq data
Some genes or their homologous were found to have interaction relationships in the immune-related signaling pathways that we identified.For examples,ctsl.1-bida, ctsl.1-birc2, ctsl.1-birc5, ctsl.1-bcl2l1,ctsl.1-xiap have interactions in the APOPTOSIS signaling pathway; ctsl.1-bcl2l1 also have interaction in the autophagy-animal signaling pathway.IL-1b-NFKB and IL-1b-JUN were involved inSalmonellainfection, toll-like receptor signaling pathway, AGERAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications,nod-like receptor signaling pathway, herpes simplex infection, and mitogen-activated protein kinase(MAPK) signaling pathway signaling pathways; and additionally, IL-1b-NFKB1 have been found to exist in the cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway.
The experimentally determined interaction relationships of ctsl.1-cd74a, calcr-calca, and calcr-RAMP1 may play a role in the immune response of turbot spleen.CD74 is an MHC class II invariant chain present on all class II expressing cells, including monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells (DC)(Yang et al., 2017).The protein interaction of lysosomal cysteine proteases cathepsins L (ctsl) with CD74 play crucial roles in the degradation of the invariant chain during maturation of MHC class II molecule and antigen processing (Gun?ar et al.,1999).Calcitonin-gene-related peptide (CGRP/calca homologous gene) and adrenomedullin are related peptides with distinct pharmacological profiles.The calcitonin-receptor-like receptor (CRLR/calcr homologous gene) can act as receptor for both CGRP and adrenomedullin (Nikitenko et al., 2000).Receptor activity-modifying proteins (RAMPs) were discovered as key components of the calcitonin gene-related peptide and adrenomedullin receptors(McLatchie et al., 1998).The receptor activitymodifying proteins (RAMPs) and the calcr are both required to generate adrenomedullin and CGRP(Hilairet et al., 2001).Co-transfection of bovine calcr with human RAMP2 or RAMP3 cDNAs in HEK-293 cells displayed high-affinity adrenomedullin receptors (Aiyar et al., 2002).Moreover, calcr associated with RAMP1 has high affinity for CGRP,whereas association with RAMP2 and RAMP3 results in higher affinity for adrenomedullin (Fitzsimmons et al., 2003).We can speculate that the immunerelated function of calca, calcr and RAMPs were associated with calcitonin regulated physiological activity.Overall, the maturation of MHC class II molecule, antigen processing and calcitonin or adrenomedullin regulated physiological activity were the main immune responses of turbot againstV.anguillaruminfection in spleen.
In gills, the immune mechanism of turbot againstV.anguillaruminfection was different from that of spleen due to the different protein interactions, such as IL-1b-IL1RAP, inhbaa-acvr1c, inhbaa-acvr2bb,fstl3-inhbaa, sh3gl2a-amph, and sh3gl2a-synjl, etc.IL-1RAP is an essential signal-transducing component of the functional IL-1R.Previous work has demonstrated that the complex formed by IL-1R and IL-1RAP is required for the signal transduction by IL-1 agonists and it has a high affinity for binding IL-1b (Cullinan et al., 1998).IL-1b, a typical cytokine,can trigger pro-inflammatory immune response in infections (Karbalaei et al., 2020).The inhibins(inhbaa, inha) cannot interact with ActRI (activin type II receptor/ACVR2) directly or after it has formed a complex with the ActRII (activin type II receptor).The activin-receptor complex is the primary target for inhibin action (Martens et al.,1997).Previous studies have shown that inhibins(inhbaa, inha), activins (acvr1c, acvr2bb), and follistatins (fsta, fstl3) are engaged in TGF-β signaling pathway, which regulate reproductive functions, wound healing, tissue regeneration, and immune system function in humans (Thompson et al., 2005).A 43-amino acid region on amphiphysin(amph) I and II may contain a SH3 binding site capable of binding to the SH3 domain on sh3gl, a homologous protein belonging to the endorphin family.Endophilin is synaptic enriched protein associated with synaptic vesicle endocytosis(Micheva et al., 1997).Synaptojanin 1 (synjl) has phosphatidylinositol phosphatase activity, capable of binds to amphiphysin and to the endophilin family(Cestra et al., 1999).The protein interactions of amphiphysin (amph), synaptojanin (synj1) and SH3-domain GRB2-likes (sh3gl1a, sh3gl1b, sh3gl2a)proteins are involved in the mechanisms of regulated endocytosis in synapses and certain endocrine cell types (Modregger et al., 2003).Altogether, the production of inflammatory factors, protein interactions of inhibins, activins and follistatins in TGF-β signaling pathway, and amphiphysin, synaptojanin and SH3-domain GRB2-likes proteins participate in the endocytosis regulation mechanism were the important events involving the immunity of turbot againstV.anguillaruminfection.
The experimentally determined interaction relationships have laid a foundation for our in-depth research on the immune mechanism of turbot againstV.anguillaruminfection.However, the interaction relationships of text mining, phylogenetic and coexpression need more experimental-verification.The way organisms resist pathogen invasion is intricate and there are numerous unbeknown interaction mechanisms waiting to be explored.
5 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, transcriptome analysis on turbot infected withV.anguillarumwas carried out and several immune-related genes were extensively determined.The clustering of differentially expressed genes, enrichment of signaling pathways and construction of PPI networks support the prediction of immune mechanisms in the spleen and gills of turbot.The findings of this study shed light on the immune response of turbot toV.anguillaruminfection, which may assist in developing effective treatments for such deadly fish disease.
6 DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
All raw data of transcriptome in the study were submitted to National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Sequence Read Archive(SRA) under accession numbers SRR14508918,SRR14508919, SRR14583691, and SRR14583690.All the other data supporting the findings of this study are available from the article and its supplementary files.
 Journal of Oceanology and Limnology2024年1期
Journal of Oceanology and Limnology2024年1期
- Journal of Oceanology and Limnology的其它文章
- Contrasts of bimodal tropical instability waves (TIWs)-induced wind stress perturbations in the Pacific Ocean among observations, ocean models, and coupled climate models*
- Variability of the Pacific subtropical cells under global warming in CMIP6 models*
- Identification of thermal front dynamics in the northern Malacca Strait using ROMS 3D-model*
- Magmatic-tectonic response of the South China Craton to the Paleo-Pacific subduction during the Triassic: a new viewpoint based on Well NK-1*
- An improved positioning model of deep-seafloor datum point at large incidence angle*
- Microplastics in sediment of the Three Gorges Reservoir:abundance and characteristics under different environmental conditions*
